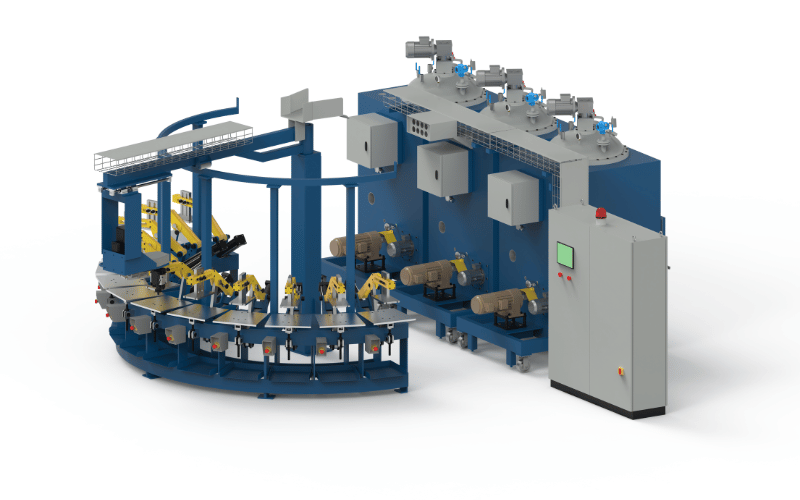
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a foundational material that shapes our daily lives, providing comfort in our homes and safety in our vehicles. The increasing global demand for high-quality foam drives the need for advanced foam production lines. These automated systems are the backbone of modern PU foam production, ensuring that manufacturers can meet market demands with speed and precision. Unlike manual methods, a dedicated production line guarantees consistency in density and structure, which is vital for strict quality control. Polyurethane foam manufacturing relies on these scalable solutions to efficiently transform volatile raw chemicals into finished products.
Key industries relying on PU foam include:
- Automotive: For seat cushions, headrests, and sound dampening.
- Construction: For thermal insulation boards and sealants.
- Furniture: For mattresses, sofas, and upholstery.
Overview of PU Foam
Polyurethane foam is a versatile polymer created through the chemical reaction of diisocyanates and polyols. This chemical flexibility allows manufacturers to engineer specific polyurethane foam properties, ranging from soft and cushioning to rigid and structural. Key PU foam characteristics include excellent thermal insulation, sound absorption, and durability. Its ability to be molded into complex shapes or produced in continuous blocks makes it a preferred material across diverse sectors, effectively bridging the gap between lightweight design and robust mechanical performance.
Importance of Production Lines in Foam Manufacturing
Implementing a dedicated production line is essential for maximizing foam production efficiency. These systems streamline the complex chemical reactions required to create foam, significantly reducing the margin for human error that leads to defects. By precisely controlling temperatures, pressures, and mix ratios, automated lines ensure a uniform product batch after batch. Automated foam manufacturing also minimizes raw material waste, which is a significant cost factor in the chemical industry. For large-scale operations, the speed and reliability of a continuous line are unmatched, turning a volatile chemical process into a stable, high-output industrial operation.
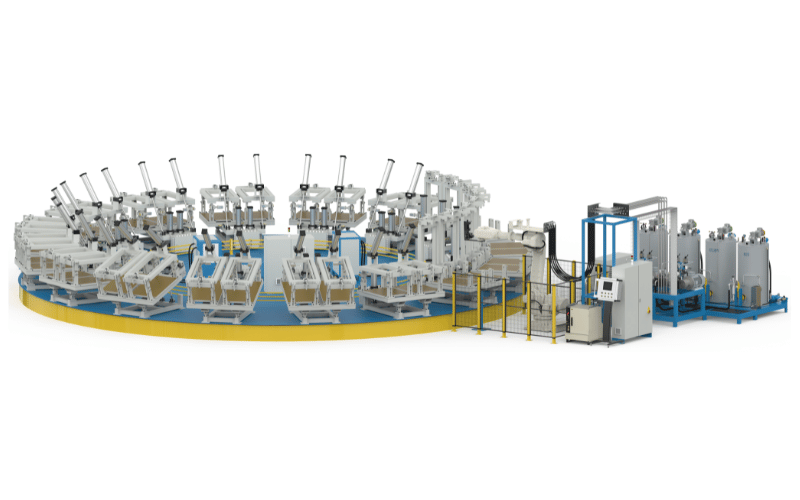
Types of Foaming Production Processes
Manufacturing needs vary significantly, leading to distinct production methods. The continuous foaming process is the industry standard for high-volume slabstock, producing long, continuous foam blocks that are later cut to size. Conversely, batch foaming is better suited for smaller, specialized runs or molded parts where formulations change frequently. Spray foam production focuses on on-site application or coating, often used in construction.
Advantages of different processes include:
- Continuous Foaming: Highest output, lowest cost per unit, consistent quality.
- Batch Foaming: High flexibility for custom formulas, lower initial setup cost.
- Spray Foaming: Seamless application, excellent for irregular surfaces and insulation.
Key Components of a Polyurethane Foam Production Line
To produce high-quality polyurethane foam, it’s essential to understand the key components of a production line. Each piece of equipment, from mixing heads to curing ovens, plays a critical role in ensuring precision, consistency, and efficiency. Let’s take a closer look at the essential components of a PU foam production line and how they contribute to the manufacturing process.
Basic Components of PU Foam Production Lines
A successful manufacturing operation relies on integrated PU foam production equipment. Each component plays a vital role in the chemical transformation.
|
Component |
Function |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Mixing Head |
Blends polyols and isocyanates. |
Ensures a homogenous mixture for a consistent foam structure. |
|
Conveyor System |
Transports the rising foam. |
Controls production speed and foam shape. |
|
Curing Oven |
Applies heat to the foam. |
Stabilizes the chemical reaction and ensures proper setting. |
|
Metering Pumps |
Delivers precise chemical amounts. |
Critical for maintaining the correct chemical ratio. |
Role of Raw Materials in Foam Production
The quality of the final product starts with the raw materials for PU foam. The precise ratio of polyols and isocyanates determines whether the foam becomes a soft mattress component or a rigid insulation board. Additives such as catalysts, surfactants, and blowing agents are crucial ingredients in polyurethane foam that control reaction rate and cell structure. Using high-purity inputs is non-negotiable; impurities or incorrect ratios can lead to structural collapse, scorching, or inconsistent density, rendering the foam unusable for commercial applications.
Understanding Foam Making Machinery
Modern PU foam production technology utilizes specific machinery to automate every step of the process. Foam-making machines must handle aggressive chemicals and high pressures safely.
Key machines include:
- Foam Dispensers: Accurately meter and mix the liquid components.
- Cutting Machines: Slice the cured foam blocks into sheets or specific shapes.
- Curing Systems: Provide the necessary environment for the foam to reach full strength.
- Storage Tanks: Maintain chemicals at the optimal temperature before processing.
Types of PU Foam Production Lines
Polyurethane foam production lines come in various configurations, each tailored to specific manufacturing needs. Whether producing high volumes of slabstock foam or crafting flexible materials for comfort products, the choice of production line impacts efficiency, quality, and cost. Let’s explore the different types of PU foam production lines and their unique features.
| Type of Production Line | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Mold Foaming Liner Production Line | Affordable and efficient for small-scale production. | View More |
| Polyurethane Mold Foaming Disk Production Line | Fully automated system for medium to large batch sizes, maximizing efficiency. | View More |
| Polyurethane Mold Foaming Semicircular Line | Simple structure and manual operation for small-scale production. | View More |
| Polyurethane Mold Foaming Ground Rail Production Line | Advanced technology for mass production of medium- to large-sized products. | View More |
| Polyurethane Mold Foaming Oval Production Line | Ideal for small-batch production, with reduced heating-oven processing times. | View More |
Continuous Polyurethane Foam Production Line
A continuous polyurethane foam production line is the primary method for high-volume foam manufacturing. In this setup, chemicals are mixed and dispensed onto a moving conveyor with side walls, allowing the foam to rise and cure as it travels down the “tunnel.” This method produces “endless” blocks of foam, known as slabstock, which can be cut to any length. It is the most efficient method for producing mattress cores and furniture cushioning, offering the lowest per-unit operating cost due to its non-stop capability.
Automatic Continuous Polyurethane Foam Production
Upgrading to fully automatic systems enhances the use of continuous PU foam technology. Automated foam production removes manual variables, ensuring that the chemical laydown is perfect every time.
Key features of automated systems include:
- Real-time Monitoring: Sensors track pressure and temperature deviations.
- Automatic Recipe Adjustment: The system alters flow rates to maintain ratios without stopping.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Fewer operators are needed to manage the line.
- Consistent Quality: Eliminates human error in mixing and pouring.
Flexible Foam Production Lines
Flexible foam production lines are specifically engineered to create soft, resilient materials used in comfort products. Unlike rigid foam lines, these systems prioritize control of cell structure to ensure breathability and elasticity. PU foam for furniture requires precise chemical metering to achieve the desired “comfort factor” and density. These lines often feature specialized “fall plate” conveyors that handle the delicate foam gently as it rises, preventing deformation and density gradients before it fully cures.
Manufacturing Processes in Foam Production
The manufacturing processes in foam production are the backbone of creating high-quality polyurethane products. From continuous foaming techniques to advanced automation and specialized sponge production, each method is designed to optimize efficiency, precision, and versatility. Let’s dive into the key processes and technologies that drive modern foam manufacturing.
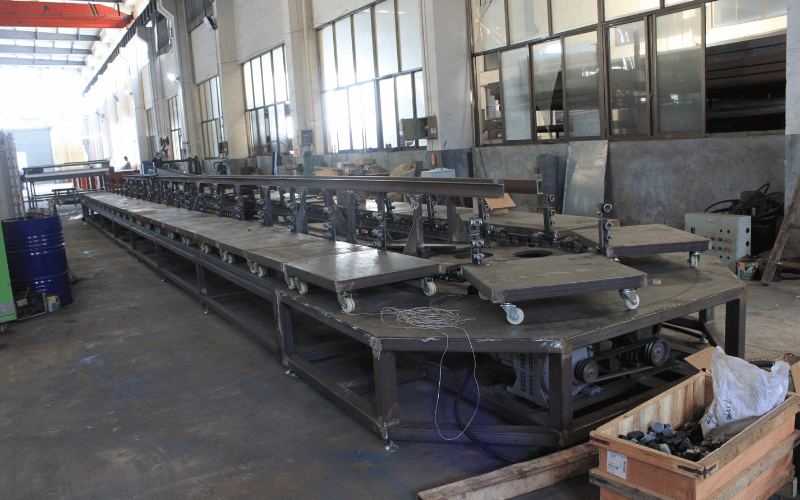

Continuous Foaming Techniques
Continuous foaming methods use a “trough” or “liquid laydown” technique, in which the mixture is dispensed onto a bottom paper or film. As the conveyor moves, the foam rises freely. Advanced PU foam production techniques use “Maxfoam” or “Varimax” technologies, which feed the chemical mix from the bottom of a trough to reduce density gradients and improve the block’s rectangular shape. This scalability enables factories to produce miles of foam blocks daily, maximizing throughput and material use.
Foam Making Machines: Automation in Production
Automated foam making relies on sophisticated PU foam machinery to control the highly exothermic reaction of polyurethane. Automation is not just about speed; it is about safety and precision.
Key automated processes include:
- Precision Metering: High-pressure pumps deliver chemicals with an error margin of <1%.
- HMI Control Panels: Operators manage the entire line from a central touchscreen.
- Automated Saws: Cutting systems trim the foam block to length while it is still moving.
- Robotic Handling: Automated arms stack and move cured foam blocks to storage.
Sponge Production and Its Applications
The sponge production process is a specialized subset of PU manufacturing, often involving a reticulation step to open the cell pores. This removes cell membranes, creating a highly porous structure ideal for absorption and filtration. PU sponge applications extend far beyond kitchen cleaning; they are widely used in acoustic soundproofing, ceramic filtration, and protective packaging. The machinery for this must be capable of handling the post-processing thermal or chemical reticulation steps required to create the unique texture of sponges.
Applications of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam’s versatility has made it indispensable across a wide range of industries. From providing superior insulation in construction to revolutionizing comfort in bedding and offering innovative solutions like spray foam, its applications are as diverse as they are impactful. Let’s explore the key uses of polyurethane foam and the unique benefits it brings to each sector.
Insulation and Its Importance
Rigid PU foam insulation is a critical component in green building strategies. Its closed-cell structure traps gas, providing one of the highest R-values per inch of any insulation material. Using polyurethane for energy efficiency significantly lowers heating and cooling costs in residential and commercial buildings. Beyond thermal regulation, these rigid foams also offer excellent structural rigidity and moisture resistance, making them essential for roofing panels, refrigeration units, and insulated wall systems.
Uses of Mattress Foam in the Industry
The bedding industry is the largest consumer of flexible foam. Polyurethane for bedding revolutionized sleep comfort by offering durable, supportive alternatives to traditional springs. PU foam mattresses can be engineered with layers of varying densities to provide specific ergonomic support.
Standard mattress foam types include:
- Memory Foam: Viscoelastic foam that contours to the body.
- High-Resilience (HR) Foam: Durable foam offering superior support and bounce.
- Standard Polyether Foam: Cost-effective foam used for base layers.
Spray Foam Applications
Spray foam insulation offers unique advantages by expanding to fill cracks and voids that traditional boards cannot reach. PU spray foam uses include sealing attics, crawl spaces, and wall cavities to create an airtight building envelope. This application not only insulates but also adds structural strength to walls and prevents moisture ingress. The equipment is portable, allowing contractors to bring high-pressure production capabilities directly to the job site.
Choosing a Supplier for PU Foam Production Lines
Selecting the right supplier for PU foam production lines is a pivotal decision that can significantly impact your manufacturing efficiency and product quality. Beyond the machinery itself, factors like technical expertise, customization options, and after-sales support play a crucial role in ensuring long-term success. Let’s delve into the key considerations, wholesale opportunities, and reliability factors to guide your supplier selection process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Supplier
Proper selection of PU foam suppliers is critical for long-term success. You aren’t just buying a machine; you are buying a partnership that dictates your production capability. Choosing foam production equipment requires careful vetting.
Key factors include:
- Technical Expertise: Do they understand your specific chemical formulations?
- Customization Capabilities: Can they tailor the line to your factory layout?
- Warranty Terms: Is the equipment covered for critical component failures?
- Local Support: Do they have technicians available in your region?
Wholesale Options for Foam Production Machinery
For large enterprises, sourcing wholesale foam machinery can lead to substantial capital savings. Working directly with major PU foam equipment suppliers allows for bulk orders of spare parts and modular upgrades at reduced rates. Wholesale purchasing often opens the door to deeper customization options, where the manufacturer tailors the entire line layout to fit specific factory floor plans and production targets, ensuring the equipment is optimized for the particular business model.
Evaluating Supplier Reliability and Quality
Investing in quality foam production equipment requires vetting the manufacturer’s track record. Reliable PU foam suppliers will offer comprehensive after-sales support, including on-site installation and operator training. Availability of spare parts is crucial; a supplier with a local inventory can prevent weeks of costly downtime. Look for suppliers that offer remote troubleshooting and regular software updates to keep the production line running at peak efficiency for years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PU foam production line, and how does it work?
A PU foam production line is an integrated set of equipment and machinery — including foam machine components, material tanks, a control system (often a PLC), a conveyor belt, molds, and foaming equipment — designed for continuous production of polyurethane foam and flexible polyurethane. The process mixes polyol and isocyanate according to a formula, meters the reactants, and injects them via a polyurethane foaming machine or casting machine into molds or onto liner paper, where the foaming process and curing produce flexible foam, mattress foam, memory foam, or insulation panels with specified density and hardness.
What types of foam machines are available for flexible PU foam manufacturing?
Manufacturers supply multiple options: automatic polyurethane foam machines for continuous foaming, high-pressure PU foam machines, continuous foaming machines, and foam-making machines for batch or casting processes. Choices range from compact injection systems to complete production lines with stainless steel material tanks, precision metering, PLC control, and conveyor belts for high-performance, automated foam production adapted to different product specifications, such as cushion, mattress foam, or rebound sponges.
How do I choose a manufacturer or supplier for PU foam production lines?
Selecting PU foam production line manufacturers involves evaluating experience, design concept, production efficiency, and after-sales support. Leading PU foam machine manufacturers (including China PU foam production line suppliers) should provide detailed specifications, options for automatic continuous polyurethane foam production, quality stainless steel material tanks, a reliable control system, testing for density and rebound, and references for flexible polyurethane or memory foam production. Consider whether you need complete production lines, spare parts, or custom formula integration.
What production outputs and product specifications can a continuous polyurethane foam production line achieve?
A modern foam production line can produce polyurethane flexible foam, memory foam, mattress foam, insulation, and special rebound sponges across a range of densities and hardness levels. Production outputs depend on foaming equipment capacity, continuous vs. batch design, meter precision, conveyor speed, mold size, and PLC-controlled parameters; manufacturers typically provide specification sheets showing density range, block length, production efficiency, and expected rebound (slow rebound vs high rebound) for different formulations.
What role do the control system and formula play in foam making?
The control system (PLC or advanced automation) precisely meters raw material flow from material tanks, controls mixing heads on PU foam machines, adjusts temperature and injection timing, and ensures repeatable foam quality. The formula — ratios of polyols, isocyanates, catalysts, surfactants, and additives — determines foaming process behavior, density, hardness, rebound characteristics, and risk of polyurethane foam collapse. Together, they deliver consistent high-quality output aligned to production needs and product specifications.
How do manufacturers prevent common problems like polyurethane foam collapse or poor rebound?
Prevention relies on optimized formulas, accurate metering, stable temperatures in material tanks, proper mixing in the polyurethane foaming machine, timely demolding, and appropriate selection of mold and liner paper. High-performance foaming equipment with precision meters and PLC control helps avoid gas loss or collapse; additives and process tuning address slow rebound or low rebound issues. Recycling off-cuts and waste improves sustainability while maintaining production quality when handled correctly.
Can a PU foam production line be automated for continuous production, and what are the benefits?
Yes, automatic continuous polyurethane foam production lines integrate foam machines, conveyors, PLC control, metering systems, and foaming equipment to run 24/7. Automation increases production efficiency, improves precision in density and hardness, reduces labor, and ensures consistent product specifications, such as memory foam or flexible polyurethane cushions. It also enables scaled manufacturing for wholesale operations and complex designs from leading PU machine manufacturers.
What are the environmental and recycling considerations for foam production?
Sustainable practices include minimizing waste through optimized formulas and precision metering, recycling trim and off-cuts into rebond or filler applications, and selecting suppliers that offer recyclable liners and energy-efficient production equipment. Proper handling of raw materials and emissions controls in the production process helps meet regulations while maintaining high-quality foam and reducing the environmental footprint of flexible PU foam manufacturing.
How do production lines differ between China PU foam production line manufacturers and other machine manufacturers?
China PU foam production line manufacturers often offer competitive pricing, a wide range of production lines from basic foam machines to complete automatic continuous foaming setups, and flexibility for custom specifications. Differences may appear in component sourcing, PLC brands, stainless steel quality of material tanks, precision meters, and after-sales service. Evaluating product specifications, performance data (density, rebound, hardness), and references for polyurethane flexible foam production helps choose the right partner for your production needs.