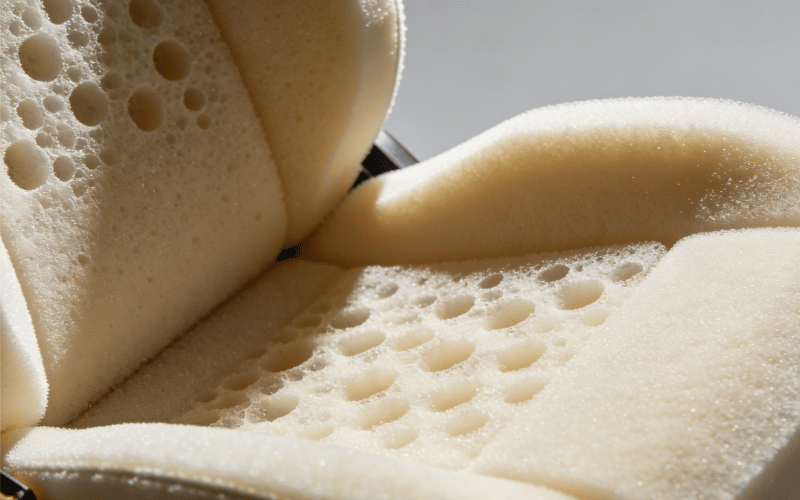
Foam production is a critical manufacturing process that transforms liquid chemicals into versatile, lightweight materials used across countless industries. The foam production process is essential for creating products that offer cushioning, insulation, and structural support. In seat foam manufacturing, this process is refined to produce ergonomic and durable seating for vehicles. Modern foam production equipment ensures consistency and quality, making it a cornerstone of high-volume manufacturing.
Key industries relying on foam production include:
- Automotive: For seats, headrests, and interior trim.
- Furniture: In mattresses, sofas, and office chairs.
- Packaging: For protective inserts that safeguard fragile goods.
- Footwear: In cushioned midsoles and insoles.
What is Foam Production?
Foam production is the process of creating a cellular structure in a liquid polymer, which then solidifies. This is achieved by introducing a gas or chemical blowing agent into the liquid mixture, which causes it to expand and form a matrix of interconnected or closed cells.
Chemical Composition of Foam
Most commercial foams, especially for seating, are made from polyurethane. This involves a chemical reaction between two primary components: a polyol and an isocyanate. When mixed, these chemicals react to form the polyurethane polymer while a blowing agent creates the foam structure.
How Foam is Manufactured
The manufacturing process involves precisely metering the liquid components, mixing them at high speeds, and dispensing the reacting mixture into a mold. The mixture then expands to fill the mold cavity and cures, solidifying into the final foam part.

Types of Foam Used in Automotive Applications
The automotive industry uses various foams to meet specific performance requirements. Polyurethane foam for car seats is the most common due to its balance of comfort, durability, and cost. However, other automotive foam types are also used.
|
Foam Type |
Durability |
Flexibility |
Cost |
Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Polyurethane (PU) |
High |
Excellent |
Moderate |
Car seats, headliners |
|
Memory Foam |
Moderate |
Superior (Viscoelastic) |
High |
Luxury seat toppers, lumbar support |
|
Latex Foam |
Very High |
High |
Very High |
Premium seating, anti-vibration pads |
|
Polypropylene (EPP) |
Excellent |
Moderate (Rigid) |
Moderate |
Impact absorption, structural components |
Importance of Seat Foam in Automobile Manufacturing
Automotive seat foam is far more than just a cushion; it is a critical component that directly impacts the driving experience and vehicle safety. The design and quality of the seat foam influence how a driver feels after hours on the road and how they are protected in a collision. High-quality foam is engineered to provide support where it’s needed most, reducing fatigue and improving posture.
Key seat foam benefits include:
- Ergonomic Support: Distributes body weight evenly to prevent pressure points and discomfort.
- Shock Absorption: Dampens road vibrations, providing a smoother ride.
- Safety: Absorbs impact energy during a crash, reducing the risk of injury.
- Noise Reduction: Helps insulate the cabin from road and engine noise.
- Design Freedom: Can be molded into complex shapes to fit modern vehicle interiors.
Components of a Seat Foam Production Line
To fully understand the intricacies of seat foam production, it’s essential to explore the components that make up a modern production line. Each machine and process plays a critical role in transforming raw materials into high-quality foam products. From chemical storage to robotic trimming, these specialized systems work in harmony to ensure precision, efficiency, and consistency throughout the manufacturing process. Let’s dive into the key machines and their functions within a seat foam production line.
Key Machines in Foam Production
A modern production line is a synchronized system of specialized foam production machines. Each piece of seat foam equipment performs a specific task to ensure the final product meets exact specifications.
- Chemical Storage and Conditioning Units: These tanks hold the raw polyol and isocyanate and maintain them at precise temperatures.
- Metering and Mixing Machines: The heart of the line, these units precisely measure and blend the chemicals before dispensing.
- Molding Conveyor System: A carousel or track that carries the molds through the filling, curing, and demolding stations.
- Mold Release Agent Sprayers: Automated systems that coat the molds to ensure easy removal of the cured foam part.
- Curing Ovens: Tunnels that maintain a controlled temperature to ensure the foam cures properly and develops its final properties.
- Robotic Demolding and Trimming: Robots that automatically remove the finished parts from the molds and trim any excess material (flash).
Role of Polyurethane in Foam Manufacturing
Polyurethane is the material of choice for polyurethane foam manufacturing due to its incredible versatility. By adjusting the chemical formula, manufacturers can create foams that are soft and flexible or rigid and strong. In polyurethane seat foam, the goal is a “high-resilience” (HR) foam that offers a perfect balance of soft initial touch and firm underlying support. It is also durable enough to withstand years of compression and cost-effective for mass production.
Equipment for Continuous Foaming
While seat foam is typically made using a discontinuous molding process, continuous foaming machines are used to produce large blocks or “buns” of foam. This automated foam production method is highly efficient for producing foam sheets for other applications.
Key features include:
- A traversing mix head that moves back and forth, pouring a continuous stream of reacting liquid onto a moving conveyor.
- Side walls on the conveyor that contain the foam as it rises.
- A long curing tunnel where the foam block solidifies.
Process of Seat Foam Production
The process of seat foam production is a blend of precision engineering and chemical expertise, ensuring that every foam cushion meets strict quality standards. From preparing molds to post-processing, each step is designed to optimize efficiency and consistency. Let’s take a closer look at the detailed steps involved in transforming raw materials into durable, high-performance seat foam cushions.
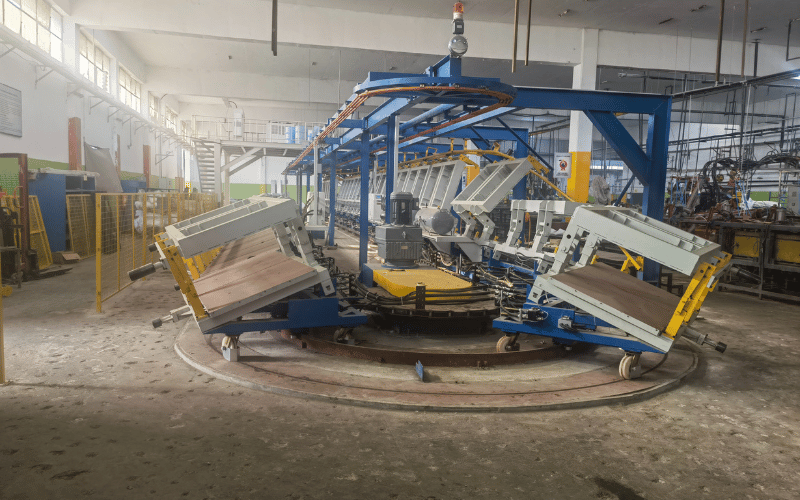
Steps in the Foam Making Process
The seat foam manufacturing process is a carefully orchestrated sequence. These foam production steps ensure that every seat produced is identical in quality and performance.
- Mold Preparation: An aluminum or steel mold is cleaned and sprayed with a release agent.
- Mixing: The polyol and isocyanate are precisely metered and blended in a high-pressure mix head.
- Pouring: The reacting liquid mixture is dispensed into the open mold.
- Molding: The mold is closed, and the foam expands to fill the entire cavity.
- Curing: The mold is placed in a heated oven for several minutes, allowing the foam to solidify and develop its physical properties.
- Demolding: The mold opens, and the finished foam cushion is removed.
- Post-Processing: The part is inspected, trimmed, and may undergo a final curing or crushing process to open its cells.
High-Pressure Molding Techniques
High-pressure foam molding is the standard for automotive seating. This technique involves injecting the chemical mixture into a closed mold at high speeds. The benefits are significant: the turbulent flow ensures a comprehensive mix, leading to a more uniform cell structure and better overall foam quality. High-pressure systems also feature self-cleaning mix heads, which reduce downtime and eliminate the need for hazardous chemical solvents, making seat foam molding techniques more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Customization of Foam for Car Seats
Automakers offer a wide variety of vehicles, each with a unique interior design. Custom seat foam allows manufacturers to create seats that are not only comfortable but also match the brand’s aesthetic and performance goals. Car seat foam customization can be achieved in several ways. For example, a luxury sedan may use a softer, lower-density foam for a plush feel. In contrast, a sports car will use a higher-density, firmer foam to provide lateral support during aggressive cornering. Dual-density foams, with a soft top layer and a firm base, are also standard for combining comfort with support.
Benefits of Automatic Foam Production
The shift to automated foam production has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, offering unparalleled advantages in efficiency, precision, and cost savings. By integrating advanced machinery and robotics, manufacturers can achieve higher output and consistent quality while reducing labor and material waste. Let’s explore the specific benefits of automation and how it transforms the foam production process.
Advantages of Automation in Manufacturing
Automated foam production offers a clear competitive advantage. By replacing manual labor with robotics and advanced machinery, automation in manufacturing leads to significant improvements across the board.
Key benefits include:
- Consistency: Machines perform the same task perfectly every time, eliminating human error and product variability.
- Speed: Automated lines can run 24/7 at high speeds, dramatically increasing output.
- Reduced Labor Costs: A single operator can oversee an entire line, lowering payroll expenses.
- Enhanced Safety: Robots handle chemicals and hot molds, protecting workers from hazardous conditions.
Efficiency of Continuous Foaming Machines
While not typically used for molded seats, continuous foaming technology exemplifies efficient foam production. These machines produce massive foam blocks with minimal waste. The process runs without interruption, maximizing material yield and throughput. The consistent mixing and pouring result in foam with uniform density from one end of the block to the other, which is crucial for applications requiring large, consistent sheets of foam.
Cost-Effectiveness in Seat Foam Production
Automation is a key driver of cost-effective foam production. For example, precise metering systems reduce chemical waste by ensuring the exact amount is used for each part. Robotic demolding reduces the labor needed per line and minimizes damage to finished parts. Lowering seat foam manufacturing costs through efficiency allows automakers to offer comfortable, high-quality seating even in economy-class vehicles, enhancing their value proposition.
Choosing a Supplier for Foam Production Equipment
Choosing the right supplier for foam production equipment is more than just a purchase—it’s a partnership that can define the success of your manufacturing operations. A well-chosen supplier not only provides high-quality machinery but also offers the expertise, support, and customization needed to optimize your production line. Let’s delve into the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier and how their reliability and tailored solutions can make all the difference.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Supplier
Selecting the right foam equipment supplier is a critical decision that will impact your production for years. When choosing foam machine manufacturers, look beyond the initial price and consider the long-term value.
Supplier Selection Checklist:
- Equipment Quality and Durability: Are the machines built with high-grade components?
- Technical Expertise: Does the supplier understand your specific production needs?
- After-Sales Support: Is technical support and training readily available?
- Spare Parts Availability: Can you quickly get replacement parts to minimize downtime?
- Customization Capability: Can they tailor a solution to fit your factory layout and product mix?
Reputation and Reliability of Foam Machine Manufacturers
It is essential to partner with reliable foam machine suppliers. A manufacturer’s reputation is built on years of successful installations and satisfied customers. Before making a decision, research trusted foam equipment manufacturers by reading case studies, asking for customer references, and checking for industry certifications. A reliable supplier will stand behind their product with a solid warranty and responsive service.
Custom Solutions Offered by Suppliers
No two factories are alike. A one-size-fits-all approach rarely works for complex manufacturing lines. Reputable suppliers offer custom foam production equipment designed to meet your unique challenges. This could involve creating a compact line for a facility with limited space or integrating specialized robotics for a complex part. These tailored foam solutions ensure you get a system perfectly optimized for your production goals.
Future Trends in Foam Production for Automobiles
As the automotive industry evolves, so too does the technology and innovation behind foam production. From cutting-edge advancements in polyurethane foam to a growing emphasis on sustainability, manufacturers are adapting to meet new challenges and opportunities. Let’s explore the latest trends shaping the future of foam production and how they’re driving the industry forward.
Innovations in Polyurethane Foam Technology
The world of polyurethane is constantly evolving. Innovative foam technology focuses on creating lighter, stronger, and more comfortable materials. Recent polyurethane foam trends include the development of foams with enhanced breathability to improve climate comfort and foams with variable-density zones molded into a single part. These advancements allow for even greater customization of the seating experience.
Sustainability in Foam Production
The push for a greener automotive industry has led to significant advancements in sustainable foam production. Manufacturers are moving away from petroleum-based chemicals and toward bio-based polyols made from soy or castor oil.
Sustainable initiatives include:
- Recycling Programs: Developing methods to chemically recycle old foam back into raw materials.
- CO2 as a Blowing Agent: Using captured carbon dioxide as a physical blowing agent to reduce the carbon footprint.
- Reduced VOCs: Formulating foams with lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions for better in-cabin air quality.
Emerging Markets and Demand for Seat Foam
Global seat foam demand continues to grow, mainly driven by emerging foam markets in Asia and South America. As car ownership rises in these regions, so does the need for locally produced automotive components. This trend is pushing foam machine manufacturers to develop more cost-effective, easy-to-operate production lines that can be deployed quickly to meet this growing demand.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an automobile foaming production line, and how does it work?
An automobile foaming production line is a specialized manufacturing plant used to produce PU foam parts, such as car seat cushions, foam sheets, and molded components. The line typically includes polyurethane foaming machines, mixing heads, high- or low-pressure foam-making machines, pouring machines or injection foaming systems, and PLC control for automation. Raw materials (polyol and isocyanate) are metered and mixed, then poured or injected into molds, where foaming occurs to create seat cushions, mattress-like padding, or other interior elastomer components.
What types of polyurethane equipment are used in a foaming line?
Standard polyurethane equipment includes multi-component foam-making machines, high-pressure polyurethane foaming machines, foam molding machines, foam sheet cutters, and foam pouring machines. Machinery often features a precision mixing head, PLC control, and options for CE certification. Manufacturers supply spare parts, customized layouts, and high-performance components to optimize production efficiency and quality.
How do I choose the right machine for producing car seat foam?
Choosing a machine car seat foam system depends on production volume, foam specification (density, hardness), mold size, and desired precision. For high-volume automobile foaming production line use, consider high-pressure injection or continuous foaming lines with multi-component metering, precise mixing heads, and robust spare parts supply. For lower volumes or flexible mixing, bench-top foam-making machines or pouring machines may suffice. Verify certification, warranty, and manufacturer support from foaming production line manufacturers.
What raw materials and specifications are essential for PU foam in auto interiors?
PU foam raw material typically consists of polyol and isocyanate, sometimes with additives for flame retardancy, color, or elastomeric properties. Key specifications include density, compression set, resilience, and hardness, tailored for seat-making, cushion, or mattress applications. Accurate mix ratios and precise mixing heads are essential for achieving consistent properties and meeting automotive safety and comfort standards.
Who are reliable manufacturers of foaming production lines, and why should we consider Chinese suppliers?
Foaming production line manufacturers range from local specialists to global companies. China has many competitive suppliers offering cost-effective machinery, spare parts, and turnkey factory solutions, including customized layouts and innovative technology. When evaluating suppliers, check CE certification, production efficiency references, customer support, and whether they can customize machines for multi-component or high-pressure injection systems for automobile foaming production line projects.
How does molding foaming differ from foam sheet or cushion production?
Molding foaming (foam molding machine foaming) injects or pours reactive polyurethane into closed molds to produce shaped parts like seat cushion cores or complex interior panels, providing precise geometry and low scrap. Foam sheet production produces continuous sheets that can be cut for cushions or mattress layers. The choice affects machine selection: molding requires robust injection or pouring machines and mold tooling, while sheet production needs continuous foaming lines and cutting equipment.
What maintenance and spare parts are critical for long-term operation?
Critical spare parts include mixing head components, seals, pumps, metering valves, and PLC modules. Regular maintenance of the mixing head and high-pressure lines, and cleaning of the metering circuits, helps prevent blockages and ensure precision. Manufacturers should supply spare parts, documentation, and training to maintain production efficiency and minimize downtime in an automobile foaming production line.
Can an automobile foaming production line be customized for different production requirements?
Yes. Manufacturers commonly customize polyurethane foaming machines for different production needs: multi-component mixing for complex elastomer blends, adjustable molds for various seat-making sizes, and PLC control for process optimization. Customization can include layout planning for factory use, integration with cutting or assembly equipment, and software for precise control to meet specific specifications and certification requirements.
What quality, safety, and certification aspects should be considered?
Quality aspects include consistency of the mix, foam physical properties, and precision of cutting or molding. Safety and certification — such as CE certification and relevant automotive standards — are essential for equipment and final parts. Ensure the machinery and processes meet environmental, fire-retardancy, and occupational-safety regulations, and that manufacturers provide testing data, quality-control procedures, and documentation to support compliance.




