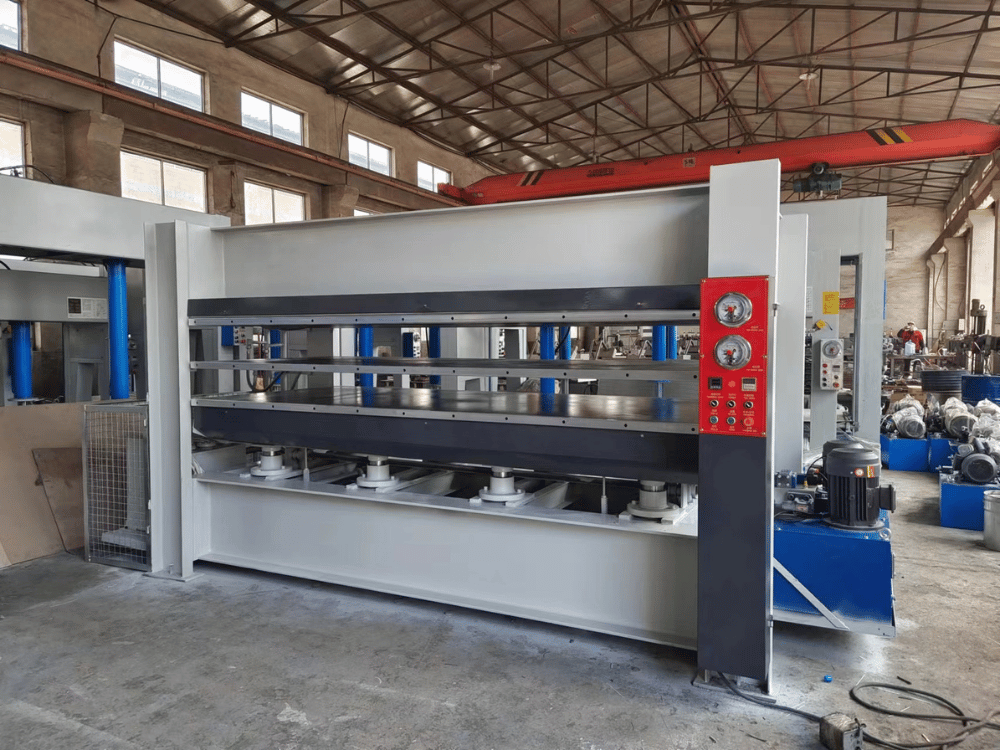
The hot press machine is a versatile and essential tool in the manufacturing industry, particularly for processing composites, polymers, and other advanced materials. This powerful equipment plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into a wide array of finished products, from automotive components and laminated wood to high-strength aerospace parts. Its ability to apply heat and pressure simultaneously enables the creation of items with superior strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy.
But what exactly is a hot press machine? How does it function to create such robust products? And what are the diverse applications where this technology is indispensable? In this blog post, we will explore the inner workings of the hot press machine, delving into its key components, operational principles, and the many industries that rely on its capabilities to produce high-quality goods.
What is a Hot Press Machine?
A hot press machine is specialized equipment designed to press, shape, and bond various materials under controlled heat and high pressure. Unlike other forming methods, the hot press uses heated plates, known as platens, to transfer thermal energy into the material while a hydraulic or electric system applies immense force. This combination facilitates chemical reactions, densification, and lamination, resulting in a solid, integrated final product. The core configuration allows for exceptional control over the manufacturing process.
The design of a hot press machine enables the efficient consolidation and curing of materials that require elevated temperatures to form. As the platens heat the raw materials placed between them, the applied pressure ensures intimate contact, eliminates voids, and shapes the material into the desired form within a mold. This process is particularly beneficial when working with thermosetting resins, composite laminates, or powder metallurgy, where heat and pressure are critical for achieving the final material properties.
The Significance of Hot Press Machines in Material Processing
In modern material processing, the hot press machine plays a vital role in achieving uniform material properties, precise shaping, and strong interlayer bonding. The machine’s ability to maintain consistent temperature and pressure across the entire surface of a part is critical for ensuring that the final product is free of defects and meets strict quality standards. This process results in parts with enhanced mechanical strength, thermal stability, and a high-quality surface finish.
One of the most significant applications of hot press technology is in the manufacturing of composite materials. For example, in the aerospace and automotive industries, carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) panels are produced using hot presses. Layers of pre-impregnated fiber sheets are stacked in a mold, which is then placed in the media. The heat activates the resin, and the pressure consolidates the layers, creating a lightweight yet powerful component. Similarly, it is used for laminating decorative surfaces onto wood panels for furniture and flooring.
Understanding the Difference Between Hot Press Machines and Cold Press Machines
Compared with cold-press machines, hot-press machines offer several distinct advantages in material processing and product quality. A cold press applies pressure at ambient temperature, primarily used for applications like bonding wood veneers with cold-set adhesives. While effective for specific tasks, it cannot cure thermosetting materials or achieve the same level of consolidation and molecular bonding as a hot press. The addition of heat in a hot press significantly accelerates curing times and enhances the material’s final properties.
The fundamental difference lies in their operational principles and resulting applications. Cold presses are simpler and consume less energy, but are limited to materials that do not require thermal activation. Hot presses, by utilizing heated platens, can process a much wider range of materials, including advanced composites, thermoplastics, and metals. The heat facilitates better resin flow, ensures complete curing, and produces parts with superior density and structural integrity. This makes hot pressing the preferred method for high-performance applications where strength and durability are paramount.
Key Components of a Hot Press Machine
The hot press machine is a complex piece of equipment with several key components that work in unison to deliver precise and repeatable results. One of the most critical elements is the set of heated plates, which are central to the machine’s function.
Heated Plates (Platens)
The heated plates, or platens, are large, flat metal blocks that transfer thermal energy to the material being processed. They are typically made from high-strength steel to withstand immense pressure without deforming. Embedded within or attached to the platens are heating elements—such as electric cartridges, thermal oil channels, or steam lines—that provide uniform temperature distribution across the entire surface. This consistency is crucial for ensuring even curing and preventing hot spots or thermal gradients that could compromise the quality of the final product.
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system is the powerhouse of the hot press, responsible for generating the massive force required for pressing and consolidation. It consists of a hydraulic pump, cylinders, valves, and a hydraulic fluid reservoir. When activated, the pump forces fluid into the cylinders, driving the movable platen towards the fixed platen and applying pressure to the material. The hydraulic system’s precision enables accurate control of closing speed, pressing force, and dwell pressure, all critical parameters in the manufacturing cycle.
Control Panel
The control panel serves as the brain of the hot press machine. Modern presses are equipped with a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) and a Human-Machine Interface (HMI), allowing operators to program and monitor every aspect of the pressing cycle. From the control panel, an operator can set and adjust the temperature of the platens, the applied pressure, the rate of pressure increase, and the cycle duration (dwell time). This level of control is essential for ensuring process repeatability and achieving consistent product quality.
Cooling System
After the heating and pressing cycle is complete, the material often needs to be cooled under pressure to solidify and stabilize its new shape. The cooling system facilitates this process by circulating a cooling medium, such as water or oil, through channels within the platens. This rapidly reduces the temperature of the part and mold, solidifying the resin or material and allowing for safe removal from the press. An efficient cooling system helps to reduce overall cycle time and improve productivity.
By understanding the functions of these key components, manufacturers can optimize the hot press machine’s performance for a wide range of materials and applications.
How Does a Hot Press Machine Work?
The working principle of a hot press machine is based on its unique ability to apply controlled heat and pressure simultaneously. This combination is essential for processing a variety of materials, from wood composites to advanced polymers. Let’s explore the step-by-step process of how a hot press machine operates.
Material Loading
The process begins with loading the raw material, or “charge,” into the press. This could be layers of composite prepreg, wood veneers coated with adhesive, or powder metal in a die. The material is carefully placed on the bottom platen, often within a mold or tool that defines the part’s final shape. Proper placement is crucial to ensure the part is formed correctly and pressure is distributed evenly.
Heating and Pressing
Once the material is loaded, the press cycle is initiated. The hydraulic system activates, causing the movable platen to close and apply an initial pressure to the material. Simultaneously, the heating system raises the temperature of the platens to a predetermined setpoint. As the material heats, it becomes pliable, allowing the resin to flow or the particles to consolidate. The pressure ensures the material conforms perfectly to the mold’s shape and eliminates any trapped air or voids.
Dwell Time
After reaching the target temperature and pressure, the machine enters the “dwell” or “curing” phase. During this time, the heat and pressure are held constant for a specific duration. This dwell time is critical for the chemical reaction (curing) to complete in thermoset materials or for the material to consolidate in other processes fully. The length of this phase depends entirely on the material type, part thickness, and desired properties.
Cooling and Ejection
Following the dwell time, the cooling cycle begins. The heating elements are turned off, and a cooling fluid is circulated through the platens to lower the mold and part temperatures rapidly. This cooling is typically done while maintaining pressure to prevent warping or dimensional changes as the material solidifies. Once cooled to a safe handling temperature, the pressure is released, the platens open, and the finished part is ejected or removed from the mold.
Post-Processing
After being removed from the press, the part may require post-processing. These can include trimming away excess material (flash) that may have squeezed out of the mold, sanding the surfaces for a smoother finish, or performing other finishing operations, such as painting or coating. These final touches prepare the component for assembly or its end-use application.
Advantages of Hot Press Machines
Hot press machines offer several distinct advantages over other manufacturing methods, making them a preferred choice for numerous industrial applications. Let’s explore some of the key benefits that hot presses provide.
- Precision and Uniformity: The ability to precisely control temperature and pressure ensures consistent material properties and dimensional accuracy, resulting in high-quality, uniform products with every cycle.
- Versatility: Hot presses can process a wide range of materials, including thermoset and thermoplastic composites, wood products, rubber, and powdered metals, making them highly adaptable.
- High Efficiency: By combining heating, pressing, and cooling in a single cycle, hot presses can significantly reduce production time. This consolidation of steps minimizes material handling and streamlines the workflow.
- Customizability: These machines can be tailored to specific product requirements, with platen sizes, pressure capacities, and heating/cooling rates that can be customized to suit unique applications.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern hot presses incorporate advanced insulation and optimized heating systems, helping minimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs during processing.
- Durability of Products: The hot pressing process creates parts with higher density, lower porosity, and stronger molecular bonds, enhancing the overall strength, longevity, and performance of the final product.
These advantages make hot press machines a powerful and efficient solution for manufacturing high-performance components across various industries.
Types of Hot Press Machines
While all hot press machines operate on the principle of applying heat and pressure, different types are designed to meet specific application needs and industry requirements. Three main categories of hot press machines are widely used in manufacturing.
Hydraulic Hot Press Machines
This is the most common type of hot press. It uses a hydraulic system to generate immense pressure, making it ideal for high-force applications. Hydraulic presses are known for their robustness and ability to deliver consistent, high-pressure over large surface areas. They are widely used in the production of plywood, particleboard, composite panels, and other applications where a high consolidation force is necessary to create dense, strong materials. Their power and reliability make them a staple in heavy-duty manufacturing.
Electric Hot Press Machines
Electric hot press machines use servo-electric actuators rather than a hydraulic system to generate pressure. This design offers exceptional precision, control, and repeatability, making it well-suited for high-tech applications in the electronics and medical device industries. Electric presses are also cleaner, quieter, and more energy-efficient than their hydraulic counterparts, as they draw significant power only during the pressing motion. Their precise control over force and position is ideal for delicate or complex components.
Vacuum Hot Press Machines
A vacuum hot press operates within an enclosed, sealed chamber from which air can be evacuated. By creating a vacuum, this type of press prevents oxidation and degradation of sensitive materials at high temperatures. This is particularly crucial in the aerospace and advanced materials sectors for processing reactive metals such as titanium and high-performance polymers. The vacuum also helps remove volatiles and trapped air from composites, resulting in a void-free part with superior structural integrity.
The Hot Press Machine From Henghui Company
The choice between these types depends on factors such as the material being processed, the required pressure, the need for environmental control, and the desired level of precision.
Applications of Hot Press Machines
Hot press machines are versatile tools that find applications across a vast range of industries due to their ability to produce strong, uniform, and high-quality parts. Let’s explore some of the key applications of this technology.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, hot presses are essential for manufacturing lightweight yet strong components that improve fuel efficiency and safety. They are used to form composite body panels, interior trim elements, and structural reinforcements from materials like carbon fiber and glass fiber. Additionally, hot pressing is the standard method for producing friction materials such as brake pads and clutch facings, where heat and pressure are used to bond various powders and fibers into a durable composite.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies heavily on hot press machines to manufacture high-performance components that meet stringent safety and performance standards. These machines are used to create lightweight structural parts from advanced composites, such as wing panels, fuselage sections, and control surfaces. The ability to produce parts with excellent strength-to-weight ratios is critical for building fuel-efficient and reliable aircraft. Vacuum hot presses are significant for processing materials that are sensitive to oxidation.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, hot presses are used for laminating multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs). Layers of copper foil and insulating prepreg are stacked and then bonded together under precise heat and pressure to create complex circuit boards. This process ensures perfect adhesion and insulation between the layers. Hot presses are also used to encapsulate electronic components and bond flexible circuits, protecting them from environmental factors and physical damage.
Construction Industry
The construction industry uses hot presses extensively to manufacture a variety of wood-based products. This includes producing plywood, particleboard, medium-density fiberboard (MDF), and high-pressure laminates (HPL) for furniture, flooring, and decorative surfaces. The machine’s ability to apply uniform heat and pressure ensures strong adhesive bonds and creates durable, dimensionally stable panels that are essential for modern building and interior design.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, hot presses are used to shape and form biocompatible materials for implants and devices. Polymers like PEEK (polyether ether ketone) and other medical-grade plastics can be molded into precise shapes for spinal implants, joint replacements, and surgical instruments. The clean and controlled environment of an electric or vacuum hot press is ideal for manufacturing sterile components that must meet strict regulatory standards for patient safety.
Final Thoughts
The hot press machine is a remarkable piece of machinery that has fundamentally shaped manufacturing processes across numerous industries. From wood and plastics to advanced composites and metals, this versatile equipment has proven its value by producing high-quality, durable, and precisely formed products. Its capacity to deliver controlled heat and immense pressure simultaneously makes it an indispensable tool for modern production, enabling the creation of components that are both strong and lightweight.
Whether you are looking to manufacture robust automotive parts, high-performance aerospace structures, or intricate electronic components, a hot press machine offers a reliable and efficient solution. By understanding its capabilities and selecting the right type for your needs, you can unlock new possibilities for innovation and product quality. The ongoing advancements in hot press technology continue to drive progress, affirming its role as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.