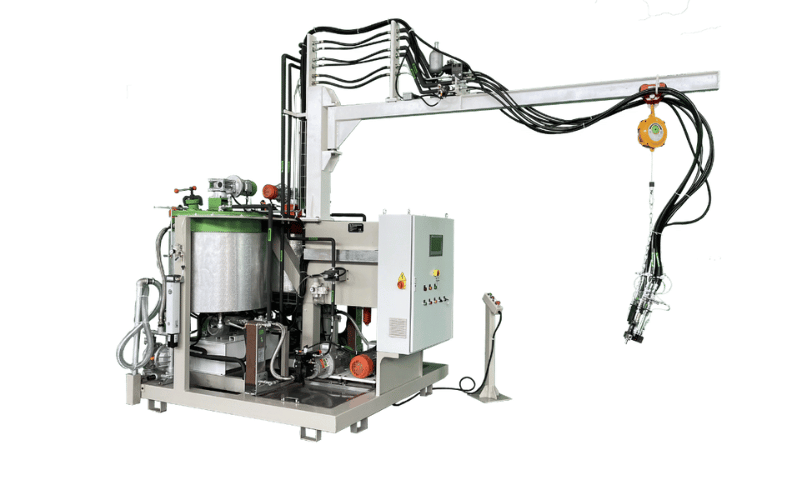
Polyurethane foam is a versatile material found in everything from building insulation to comfortable mattresses. The magic behind its creation lies in specialized polyurethane foam machines. These sophisticated systems are the backbone of modern production, designed to precisely meter, mix, and spray foam components to create high-quality finished products. This guide explores the world of PU foam solutions, breaking down the machines, their essential elements, and their wide range of applications. Understanding this technology is key to unlocking efficiency and innovation in manufacturing.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a polymer created by reacting two main chemicals: a polyol and an isocyanate. The reaction produces a foam that can be either rigid or flexible. Key polyurethane foam properties include excellent thermal insulation, lightweight strength, durability, and versatility. These characteristics make it ideal for a wide range of PU foam applications, from cushioning in furniture and automotive seats to providing structural support and insulation in construction and refrigeration.
Importance of Foam Machines in Production
PU foam machine benefits are central to modern manufacturing. These machines streamline the entire production process by ensuring the chemical components are metered and mixed with extreme precision. This accuracy is critical for achieving consistent foam quality, density, and performance. By automating the application, foam machines improve foam production efficiency, reduce material waste, and minimize human error. This leads to higher quality products, lower operational costs, and a safer working environment.
Overview of Metering and Mixing Processes
The creation of polyurethane foam depends on a perfectly controlled chemical reaction. Metering systems and mixing techniques are at the heart of this process. The machine accurately measures and delivers the correct ratio of polyol and isocyanate from storage tanks to a mix head.
- Metering: High-precision pumps draw the chemicals and feed them into separate lines under controlled pressure and temperature.
- Mixing: The chemicals are forced together inside a mixing head, where they are blended intensely for a fraction of a second.
- Dispensing: The mixed liquid is then dispensed or sprayed onto a surface or into a mold, where it expands and cures into its final foam state.
Types of Polyurethane Foam Machines
Polyurethane foam machines come in various types, each tailored to specific production needs and applications. From high-pressure systems designed for large-scale manufacturing to low-pressure machines ideal for smaller projects, these technologies offer versatile solutions for creating high-quality foam. Let’s explore the different types of polyurethane foam machines and their unique features, starting with high-pressure systems.
High-Pressure Polyurethane Machines
High-pressure PU machines operate by impinging two chemical streams at pressures exceeding 1,500 PSI. This intense pressure creates a highly turbulent flow in the mix head, resulting in a comprehensive and rapid mix without a mechanical stirrer. This method is ideal for efficient foam production in high-volume applications, as it minimizes waste and reduces cleaning time. High-pressure systems are widely used for making automotive parts, insulation panels, and appliance foam.
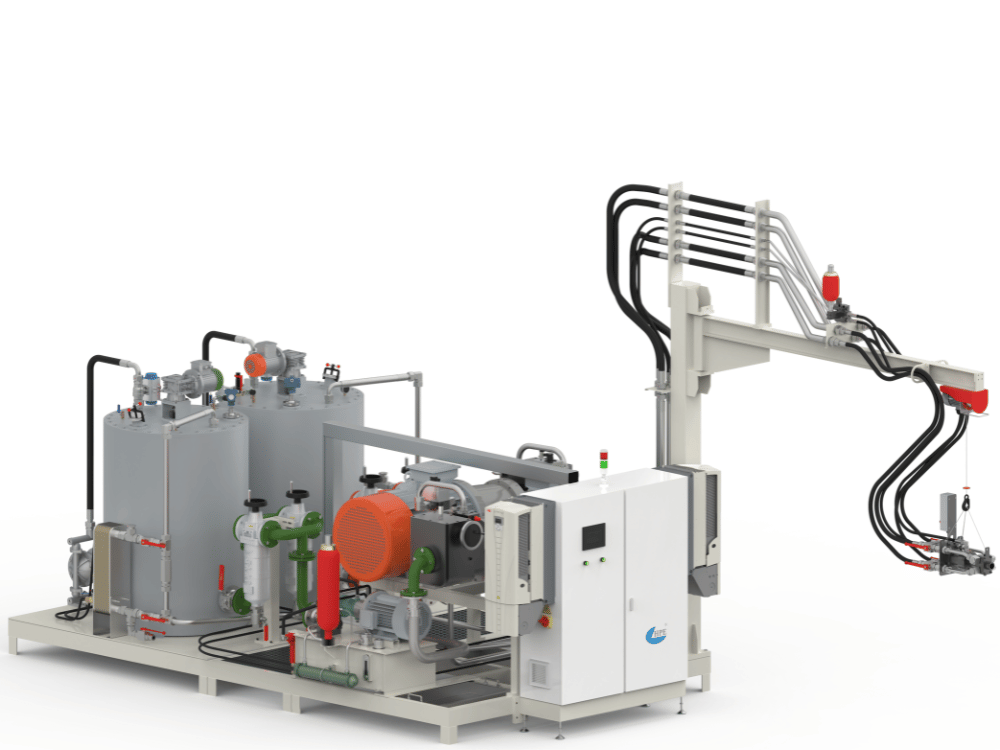
Low-Pressure PU Foaming Machines
Low-pressure foam machines operate at much lower pressures, typically below 500 PSI, and use a mechanical mixer to blend the chemicals. These machines are often more affordable and well-suited for smaller-scale production or applications that require slower pour rates. While they may require more frequent cleaning due to chemical buildup in the mix head, low-pressure systems offer versatile PU foam solutions for custom molding, prototyping, and architectural elements.
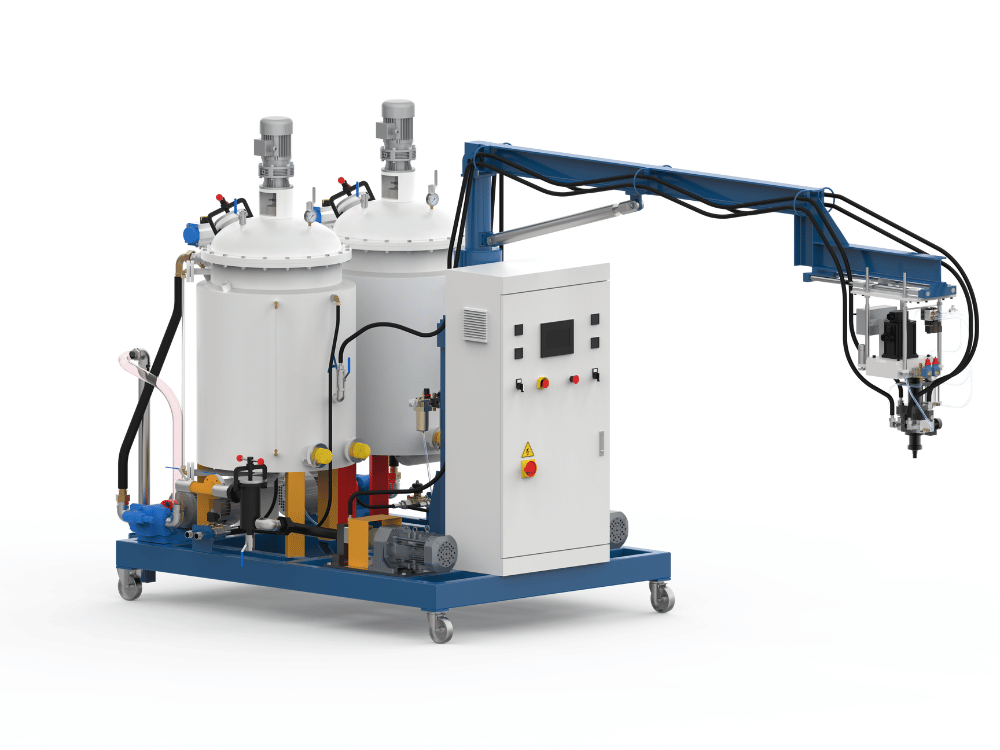
Spray Foam Machines and Their Applications
PU spray machines are portable systems designed to apply polyurethane foam directly onto surfaces. These machines heat and pump the chemicals through a heated hose to a spray gun, where they are mixed and atomized. This is the go-to technology for creating seamless insulation layers. Key applications include:
- Spray foam insulation for residential and commercial building walls, attics, and crawl spaces.
- Roofing systems to create a monolithic, waterproof barrier.
- Sealing air gaps and cracks to improve energy efficiency.
- Industrial tank and pipe insulation.
Components of a Polyurethane Foam Machine
To fully understand how polyurethane foam machines operate, it’s essential to break down their key components. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring precise metering, mixing, and application of the foam. From the mix head to the pumps and sprayer mechanism, these components work together to deliver high-quality results. Let’s take a closer look at the functionality and importance of each element in the foam production process.
Mix Heads and Their Functionality
The mix head is where the chemical reaction begins. Its primary function is to blend the polyol and isocyanate streams into a homogenous mixture before dispensing. High-pressure mix heads use impingement mixing, while low-pressure ones use a mechanical agitator. Proper mix head functionality is critical for achieving consistent cell structure and foam properties, making it one of the most essential components of PU foam mixing.
Pumps and Their Role in Foam Production
Pumps are the heart of the machine’s metering system. Foam production pumps, such as axial piston or gear pumps, are engineered for high precision. They are responsible for delivering the exact chemical ratio to the mix head. Any deviation in the PU foam metering can result in poor-quality foam. Therefore, these pumps must be reliable, accurate, and capable of maintaining consistent pressure and flow rates throughout the production cycle.
Understanding the Sprayer Mechanism
In spray foam applications, the sprayer or spray gun is the final point of control. PU foam sprayers are designed to atomize the mixed liquid chemicals into a fine mist that can be applied evenly. The design of the spray tip and the operating pressure determine the spray pattern and flow rate. Efficient spray foam application depends on a well-maintained sprayer mechanism that ensures a consistent, uniform layer of foam without drips or overspray.
Metering and Mixing in Polyurethane Processing
Metering and mixing are the backbone of polyurethane foam production, ensuring that the right chemical ratios and blending techniques are applied for consistent, high-quality results. Whether through high-pressure systems or advanced automation, these processes are critical to achieving the desired foam properties. Let’s dive into the methods and technologies that make metering and mixing in polyurethane processing so effective.
High-Pressure Metering Machines
High-pressure metering systems offer unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. By delivering chemicals at high velocity, these machines ensure a rapid and complete mix, which is crucial for fast-curing foam systems. This precision in PU foam accuracy leads to a more uniform cell structure, better physical properties, and minimal off-ratio material. The self-cleaning nature of high-pressure mix heads also reduces maintenance downtime.
Mixing Techniques for Optimal Foam Quality
Achieving optimal foam mixing is essential for producing high-quality polyurethane. The proper technique depends on the machine type and foam system.
- Impingement Mixing: Used in high-pressure machines, this technique creates a turbulent, laminar flow that results in an ultra-fine mix.
- Mechanical Mixing: Low-pressure machines use a motor-driven stirrer to blend components thoroughly.
- Static Mixing: Some systems use a disposable static mixer nozzle for small-scale applications, eliminating the need for solvent flushing.
Automation in Foam Production Lines
Automated foam production is transforming the industry. Robots can be programmed to dispense foam into complex molds with perfect repeatability, while sensors monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rates in real time. This PU foam technology improves consistency, enhances worker safety by minimizing chemical exposure, and increases throughput. Automation enables complex, multi-step processes to be executed flawlessly, reducing errors and optimizing material use.
Applications of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam’s versatility has made it a cornerstone material across a wide range of industries. From construction to consumer goods, its unique properties allow it to meet diverse needs with efficiency and reliability. Let’s explore the various applications of PU foam, starting with its critical role in insulation for the construction industry.
Insulation Uses in Construction
In construction, PU foam insulation is prized for its high thermal resistance (R-value). It is used to create airtight building envelopes, significantly reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Typical construction applications include spray foam for walls and attics, rigid foam boards for sheathing, and insulating panels for roofs and doors, providing both thermal and structural benefits.
Industrial Applications of PU Foam
The versatility of industrial PU foam makes it essential in numerous sectors. In the automotive industry, it is used for seats, headliners, and sound-dampening components. In refrigeration, its excellent insulating properties are used in refrigerators and freezers. Other key foam applications include protective packaging, marine floatation devices, and molded parts for various industrial equipment.
Consumer Products Made from Polyurethane Foam
PU foam is a staple in many everyday items due to its comfort and durability. PU foam consumer products are everywhere we look:
- Furniture: Cushions for sofas and chairs.
- Bedding: Mattresses and pillows made from memory foam.
- Footwear: Midsoles and insoles for athletic and casual shoes.
- Household Items: Sponges and novelty items.
Quality Control in Foam Production
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential in polyurethane foam production to ensure the material performs as expected across various applications. From rigorous testing methods to advanced technologies, quality control processes play a pivotal role in delivering reliable and consistent products. Let’s delve into the key aspects of foam quality measurement, testing, and enhancement.
Measuring Foam Quality Standards
Adhering to strict foam quality standards is crucial for ensuring product performance and safety. Key metrics include density, tensile strength, compression set, and thermal conductivity. Manufacturers follow ASTM or ISO standards for PU foam testing to ensure their products meet the specifications required for their intended applications, whether construction, automotive, or consumer goods.
Testing and Inspection Methods
Several foam testing methods are used to verify quality during and after production. These inspections ensure the foam meets all required physical properties.
- Density Test: Measures the weight per unit volume of the foam.
- Compression Test: Evaluates the foam’s ability to withstand a compressive force.
- Tensile and Elongation Test: Determines the foam’s strength and flexibility.
- Thermal Resistance Test: Measures the R-value for insulation applications.
Enhancing Foam Quality through Technology
Advanced foam quality technology is helping manufacturers produce better products more consistently. IoT sensors integrated into foam machines provide real-time data on processing parameters, allowing for immediate adjustments. AI algorithms can analyze this data to predict and prevent defects before they occur. These innovative PU foam solutions lead to higher yields, less waste, and a superior end product with reliable performance characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PU foaming machine, and how does it work?
A PU foaming machine mixes polyol and isocyanate through precision mixing equipment to produce rigid and flexible polyurethane foams. The modules often include metering pumps, a pneumatic or hydraulic drive, a high-pressure or low-pressure valve, and a spray gun or injection head. High-pressure polyurethane metering systems deliver accurate output for high-pressure polyurethane foaming and spray foam insulation. At the same time, low-pressure machines are used for less demanding casting and foam blocks production.
What are the differences between high-pressure PU and low-pressure machines?
High-pressure technology uses high-pressure PU metering and a high-pressure spray machine or polyurethane spray foam machine to achieve better atomization, higher output, and reliable mixing for rigid foam, elastomer, and coating applications. Low-pressure machines are user-friendly, have lower viscosity limitations, and are ideal for adhesives, some molding, and applications requiring discontinuous polyurethane processing. Choice depends on material viscosity, desired foam density, and the range of polyurethane products being manufactured.
Which components are essential in polyurethane metering machines?
Essential components include precision metering pumps for polyol and isocyanate, valves (including high-pressure and pneumatic), mixing equipment, a spray gun or injection module, a control system for output regulation, and safety devices. Quality polyurethane machinery also incorporates pneumatic or hydraulic drive modules, a low-maintenance design to reduce downtime, and options for sales, service, and technical support to ensure longevity and reliability.
What applications can a PU foaming machine serve in industry?
PU foaming machines serve a wide range of applications across the building industry, refrigeration, automotive, and composite manufacturing. They are used to insulate (spray foam insulation), produce foam blocks, make durable, lightweight parts for automotive and refrigeration applications, and castings, coatings, and elastomer components. High-pressure polyurethane spray machines are standard for spray foam insulation and high-quality polyurethane coatings, while discontinuous polyurethane systems are used for molded parts and foam blocks.
How do I choose the right machine for manufacturing rigid foam or flexible foam?
Choose based on desired foam type (rigid foam vs. flexible), production output, material viscosity, including polyol characteristics, precision required in mixing, and whether continuous or discontinuous production suits your needs. For the highest-quality rigid foam and spray applications, high-pressure polyurethane metering and a high-pressure spray gun provide better atomization and adhesion. For composite casting and adhesive applications, consider machines optimized for lower pressure and user-friendly operation.
What maintenance, downtime reduction, and reliability features should I look for?
Look for machines designed for low maintenance with easy-access modules and long-life seals. Pneumatic or hydraulic drives should be robust and serviceable. Features that reduce downtime include replaceable valve cartridges, reliable metering pumps, onboard diagnostics, and access to technical service, spare parts, and service. High-quality machinery emphasizes longevity, consistent output, and precision to ensure continuous production of quality polyurethane products.
Can a PU foaming machine handle different materials, such as epoxy, adhesives, or polyol blends?
Many polyurethane metering machines can handle a wide range of materials, including polyol blends, adhesives, and specific epoxy-compatible systems, provided the viscosity and chemical compatibility are within the machine’s specifications. High-pressure polyurethane systems are better for high-viscosity materials and high-pressure PU applications, while low-pressure machines may be preferred for sensitive adhesives or discontinuous processing. Always consult an engineer or technical service to confirm compatibility.
What safety and environmental considerations are essential when using a polyurethane spray machine?
Safety includes proper ventilation, PPE for operators, leak-free valves and hoses, controlled spray gun operation, and spill containment. Environmental considerations include accurate metering to reduce waste, selecting formulations that meet regulations, and handling polyol and isocyanate components safely. Regular training, scheduled maintenance to avoid downtime, and working with manufacturers offering sales and service support help maintain safe, reliable operations.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Polyurethane Foam Machines
Polyurethane foam machines are the backbone of efficient and high-quality foam production, seamlessly handling the critical processes of metering, mixing, and spraying. By delivering precise chemical ratios, ensuring thorough blending, and enabling versatile application methods, these machines empower manufacturers to meet the demands of diverse industries—from construction and automotive to consumer goods.
As technology continues to advance, innovations like automation, IoT integration, and AI-driven quality control are revolutionizing the capabilities of polyurethane foam machines. These advancements not only enhance production efficiency but also improve product consistency, reduce waste, and ensure compliance with stringent quality standards.
For businesses looking to stay competitive, investing in modern polyurethane foam machines is more than a choice—it’s a necessity. By embracing these cutting-edge solutions, manufacturers can optimize their operations, expand their market reach, and deliver superior products that stand the test of time.




