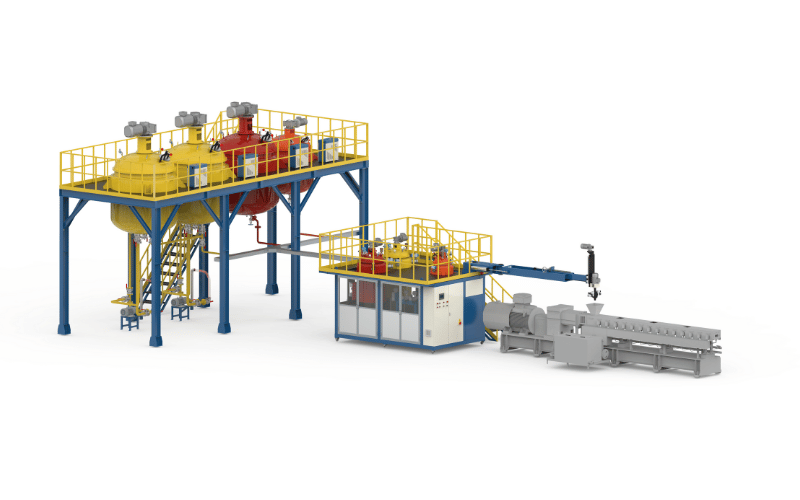
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) has become a cornerstone material in modern manufacturing, prized for its exceptional properties that bridge rubber and plastic. This versatile elastomer offers the elasticity of rubber combined with the durability and processability of thermoplastics. Efficient polyurethane processing relies heavily on advanced technology to handle this unique material. The specific TPU benefits, including high tear strength and resistance to oil and grease, make it indispensable across various sectors. However, unlocking these properties requires precise machinery capable of managing complex chemical reactions.
Key industries leveraging TPU applications include:
- Automotive: For instrument panels, gear knobs, and door handle cups.
- Footwear: In high-performance shoe soles and heel counters.
- Electronics: For durable phone cases and wire jacketing.
- Medical: Used in tubing, catheters, and flexible membranes.
What is TPU?
TPU is a class of polyurethane plastics with many valuable properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion. Chemically, it is a block copolymer consisting of alternating hard and soft segments. This unique structure confers thermoplastic polyurethane properties, allowing it to be melted and reformed like plastic but to behave like rubber at room temperature. Key TPU material characteristics include high elongation at break and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it distinct from other elastomers that cannot be reprocessed once cured.
Applications of TPU in Industry
The adaptability of TPU enables its use across a wide range of manufacturing contexts. TPU industrial uses range from heavy-duty mechanical parts to delicate medical components. In the automotive sector, it is used for noise and vibration-damping components. In the medical field, its biocompatibility makes it ideal for devices that come into contact with bodily fluids. TPU applications in manufacturing also extend to industrial hoses and drive belts, where durability is paramount.
Specific examples include:
- Sports Equipment: Ski boots and roller skate wheels that require impact resistance.
- Textiles: Waterproof and breathable films for outdoor clothing.
- Industrial Seals: High-performance gaskets that withstand harsh chemicals.
- 3D Printing: Flexible filaments for creating custom elastic parts.
Importance of Metering in TPU Processing
The quality of the final TPU product is directly tied to the precision of the manufacturing process. TPU metering accuracy is critical because the chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates must occur at exact stoichiometric ratios. Even a slight deviation can lead to material defects, such as poor elasticity or structural weakness. The importance of dosing systems lies in their ability to maintain material consistency, significantly reducing waste and ensuring that every batch meets rigorous quality standards. Without precise metering, achieving the desired physical properties of TPU is virtually impossible.
Understanding the Metering Machine
To fully appreciate the capabilities of a metering machine, it’s essential to understand its individual components and how they work together to ensure precise chemical handling. Each part, from storage tanks to control systems, plays a critical role in maintaining accuracy and efficiency. Let’s take a closer look at the key components of a metering machine and their importance in TPU processing.
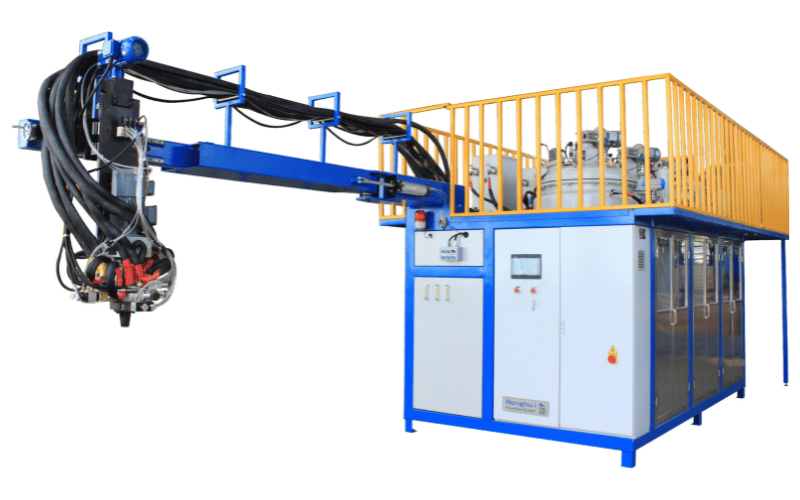

Components of a Metering Machine
A metering machine is a sophisticated assembly of parts designed to handle reactive chemicals safely and accurately. Understanding these metering machine components helps in selecting the right equipment for specific needs. The interplay between tanks, pumps, and controls defines the efficiency of TPU dosing systems.
|
Component |
Function |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Storage Tanks |
Hold raw chemical components (polyols, isocyanates). |
Maintain temperature and agitation to prevent separation. |
|
Metering Pumps |
Deliver precise volumes of chemicals. |
Ensure exact ratios for the chemical reaction. |
|
Mixing Head |
Blends the components thoroughly. |
Critical for a homogenous mixture and proper curing. |
|
Control System |
Monitors pressure, flow, and temperature. |
Allows for real-time adjustments and recipe management. |
Functionality of Dosing Systems
TPU dosing functionality centers on the precise delivery of chemical components to the mixing head. These systems use advanced software to synchronize pump speed and output, ensuring the ratio remains constant even as flow rates change. Accurate dosing systems often feature closed-loop control mechanisms that continuously monitor flow meters. If a deviation is detected, the system automatically adjusts pump speed in milliseconds. This level of automation and real-time monitoring is essential for minimizing rejected parts and maintaining high throughput in industrial environments.
Types of Pumps Used in Metering
Different TPU metering pumps are used based on material viscosity and required pressure. Selecting the correct pump is vital for consistent flow and the machine’s longevity.
- Gear Pumps: Excellent for high-viscosity materials; they provide a continuous, non-pulsing flow.
- Piston Pumps: Ideal for high-pressure applications and filled materials; they offer robust durability.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Used for low-pressure applications; they handle abrasive or shear-sensitive fluids.
- Screw Pumps: Suitable for applications requiring a gentle, pulse-free flow across a range of viscosities.
The Polyurethane Process
The polyurethane process is a carefully orchestrated series of steps that transforms raw materials into versatile and durable products. From precise chemical reactions to advanced control mechanisms, every stage plays a vital role in ensuring consistent quality and performance. Let’s delve into the key aspects of polyurethane production, including the polymerization process and the critical controls that keep everything running smoothly.
Overview of Polyurethane Production
The polyurethane production process transforms raw liquid chemicals into solid, durable elastomers. It begins with the preparation of raw materials, which are then precisely metered and mixed. This mixture is dispensed into molds or extruded onto conveyor belts, where it reacts and cures. TPU manufacturing steps often include post-curing treatments like annealing to maximize physical properties. The entire workflow requires strict environmental controls, as humidity and temperature can significantly affect the outcome.
Reactive Polymerization Process
At the heart of TPU creation is the polymerization process. This involves the reaction of diisocyanates (hard segments) with long-chain polyols (soft segments) and chain extenders. The TPU chemical process is an addition polymerization, meaning no by-products are released. The ratio of hard to soft segments determines the material’s final hardness and flexibility. Controlling this reaction rate is crucial; if it occurs too quickly, the material may not fill molds appropriately, and if it proceeds too slowly, production cycles lengthen unnecessarily.
Control Mechanisms in Polyurethane Processing
Effective TPU process control relies on a network of sensors and regulators. Temperature regulation is paramount, as it affects the viscosity and reactivity of the components. Polyurethane production monitoring systems continuously track these variables.
Key control features include:
- Pressure Monitoring: Ensures pumps are operating correctly and detects blockages in lines or mixing heads.
- Flow Control Meters: Verify that the exact amount of each component is being delivered.
- Temperature Controllers: Maintain tanks and lines at optimal heat to ensure consistent material viscosity.
- Ratio Monitoring: Alarms the operator immediately if the chemical mix deviates from the set recipe.
Extrusion and Pelletizing Systems
Extrusion and pelletizing systems are critical steps in TPU production, transforming raw materials into usable forms like pellets or films. These processes require precision and advanced technology to ensure consistent quality and efficiency. Let’s explore the role of extruders, the differences between high-pressure and low-pressure systems, and the innovative pelletizing techniques that make TPU production seamless.
Role of Extruders in TPU Production
Extruders are the workhorses in the continuous production of TPU. The TPU extrusion process involves melting the polymerized material and forcing it through a die to shape it. Extruders in polyurethane production must provide consistent heat and shear to ensure the material is homogenous without degrading the polymer chains. Precision in this step is vital for producing high-quality pellets or films that are free of bubbles and impurities.
High-Pressure vs. Low-Pressure Systems
The choice between high-pressure TPU systems and low-pressure polyurethane processing depends on the specific application and material formulation.
|
Feature |
High-Pressure Systems |
Low-Pressure Systems |
|---|---|---|
|
Mixing Energy |
High (impingement mixing). |
Low (mechanical mixing). |
|
Cleaning |
Self-cleaning; no solvents needed. |
Requires solvent flushing. |
|
Material Waste |
Minimal. |
Higher due to flush cycles. |
|
Cost |
Higher initial investment. |
Lower initial cost. |
|
Ideal Application |
High-volume, fast-cycle production. |
Smaller batches, varying viscosities. |
Pelletizing Techniques and Technologies
Once extruded, TPU must be cut into pellets for handling and further processing. TPU pelletizing methods vary depending on the material’s hardness and tackiness. Polyurethane pelletizing technologies have evolved to handle even very soft, sticky TPUs efficiently.
Common techniques include:
- Underwater Pelletizing: The die face is submerged in water; cutters slice the polymer as it emerges. The water immediately cools the pellets, preventing sticking.
- Strand Pelletizing: Strands are extruded into a water bath for cooling, then cut with a rotary knife. Best for harder TPU grades.
- Hot Die Face Pelletizing: Pellets are cut in air or mist immediately at the die face. Suitable for materials that are sensitive to water absorption.
Elastomer Casting Machines
Elastomer casting machines are at the heart of producing high-quality TPU components, offering tailored solutions for both flexible and rigid applications. From advanced extrusion technologies to specialized systems for managing high-viscosity materials, these machines ensure precision and efficiency in every step. Let’s dive deeper into the differences between flexible and rigid casting systems, the advantages of twin screw extruders, and the innovations in handling high-viscosity TPU.
Flexible vs. Rigid Casting Systems
Casting machines are tailored to the specific hardness of the final product. Flexible TPU casting systems are designed to handle lower hardness materials often used for seals or soft-touch grips. These systems prioritize gentle handling to prevent deformation during demolding. Conversely, rigid polyurethane systems are built for structural parts and require higher clamping forces and more robust molds to withstand the pressures generated by expanding, more rigid foams or solids.
Advantages of Twin Screw Extruders
Twin screw extruder benefits are significant in reactive extrusion processes. Unlike single screw systems, twin screws employ two intermeshing screws that provide superior mixing and shearing action. This leads to a more uniform distribution of additives and a more consistent molecular weight in the polymer. TPU extrusion technology utilizing twin screws offers higher throughput rates and the ability to process a broader range of viscosities, making it ideal for continuous polymerization.
High Viscosity Management in Casting
Handling thick, resistant materials is a significant challenge in casting. High viscosity TPU casting requires specialized equipment capable of generating high pressures without overheating the material. Viscosity control in polyurethane processing involves heated lines and tanks to lower viscosity, along with powerful positive displacement pumps. These systems prevent cavitation and ensure the mold is filled, capturing even the finest details of the design.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a TPU dosing machine, and how does it fit into polyurethane manufacturing?
A TPU dosing machine is specialized metering and mixing equipment used to accurately dispense thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) raw material and additives into a production process. It integrates metering pumps, flow meters, control systems, and mixers—sometimes twin-screw or piston-based—to blend resin, solvents, and other chemicals. In polyurethane manufacturing, the machine ensures precise mass flow and ratio control so that foam, elastomer processing, or cast parts achieve the required material properties and end products.
How does precision metering and mixing work in TPU dosing machines?
Precision is achieved using metering pumps, mass flow instrumentation, and closed-loop control systems that monitor flow rates, temperatures, and pressure. Metering and mixing modules may combine high-pressure pumps with dynamic mixers or static mixers to continuously blend fluids at exact ratios. Flow meters, sensors, and automation allow the machine to rotate dosing cycles, adjust output on demand, and maintain consistent reaction conditions for high-quality production.
Can TPU dosing machines operate continuously for large production lines?
Yes, many industrial TPU dosing machines are designed for continuous operation to support large-scale production lines. Continuous systems feature robust motor drives, cooling, and solvent handling, granulation or pour options, and automation to maintain stable output. Proper storage of raw material, instrumentation for temperature control, and scheduled maintenance ensure consistent performance for long production runs.
What raw materials and chemical handling considerations are required?
TPU dosing machines handle thermoplastic polyurethanes, polyols, isocyanates, solvents, and additives. Equipment must be compatible with the fluid chemistry and temperature ranges. Materials need proper storage and conditioning—keeping resin cool or at a controlled temperature prevents changes in viscosity. Chemical seals, appropriate pumps, and solvent handling systems are essential for safe, contamination-free dispensing and metering.
How do manufacturers ensure accuracy when dosing low-viscosity or high-pressure fluids?
Accuracy for low-viscosity fluids is achieved using precision metering pumps, calibrated flow meters, and temperature control to maintain a constant viscosity. For high-pressure applications, robust pumps, reinforced piping, and pressure-rated mixers are used. Techniques such as mass flow measurement, piston dosing, and feedback control minimize errors and ensure that the blend ratio remains within tight tolerances during reaction and molding stages.
What are the typical components and instrumentation on a TPU dosing machine?
Typical components include twin-screw or piston metering pumps, motor drives, flow meters, temperature sensors, control cabinets, mixers (static or dynamic), metering valves, solvent recovery systems, and optional granulation or panel pour stations. Instrumentation for pressure, temperature, and mass flow is integrated into automation and control systems to automate dosing, monitor equipment health, and certify output quality to ISO or customer standards.
How do TPU dosing machines support different end products like foam, molded parts, or panels?
Flexibility comes from interchangeable heads, adjustable metering ratios, and programmable sequences. For foam or elastomer processing, the machine meters polyol and isocyanate for reaction and expansion control; for molded parts or panels, it provides stable pour, degassing, and mold filling. Granulation or downstream cooling can be added for pelletizing thermoplastic TPU. Tailor-made setups enable the same machine to produce a range of end products by changing mold, dispense pattern, or formulation.
What maintenance and handling practices maximize uptime and output quality?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting metering pumps and seals, calibrating flow meters, cleaning mixers and solvent lines, and verifying control system parameters. Proper handling of raw materials—temperature control, moisture management, and secure storage—prevents contamination and viscosity shifts. Automated diagnostics, routine lubrication of rotating parts, and scheduled replacement of wear items such as rollers and piston seals reduce downtime and maintain high-quality output.
How do I choose a Chinese manufacturer or supplier for a TPU dosing machine?
When evaluating a Chinese manufacturer, look for proven experience in polyurethane equipment, references for industrial installations, and certifications such as ISO. Verify that they supply the specific machine technology you need—metering and mixing modules, mass flow instrumentation, high-pressure options, and automation control systems. Ask about customization, after-sales service, spare parts availability, and whether they can tailor the machine for your production line, output rates, and chemical compatibility.
Conclusion
As the polyurethane industry evolves, any discussion of TPU metering machines must highlight the innovations shaping the future and the practical considerations for manufacturers. From emerging trends in innovative technology to the critical factors in selecting the right equipment, understanding these elements ensures businesses stay competitive and sustainable. Let’s explore the advancements, decision-making tips, and key benefits that define the next generation of TPU metering technology.
Future Trends in TPU Metering Technology
The future of TPU metering is shifting towards more intelligent, more connected factories. We are seeing an increase in IoT integration, in which machines communicate real-time data to central hubs for predictive maintenance. Innovations in polyurethane processing include AI-driven algorithms that optimize flow rates and temperatures on the fly to maximize energy efficiency and product quality. Furthermore, machines are being adapted to process bio-based and recycled TPUs, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for Your Needs
Selecting the best TPU machine manufacturers involves looking beyond the price tag. Reliability and technical support are paramount. When choosing polyurethane equipment, consider manufacturers who offer robust customization options to tailor the machine to your specific material and output requirements. Look for providers with a strong track record of after-sales service, readily available spare parts, and comprehensive training programs for your operators.
Summary of Key Benefits of TPU Metering Machines
Investing in high-quality metering technology transforms production capabilities. The advantages of polyurethane processing equipment are clear and measurable.
- Precision: Exact chemical ratios ensure consistent material properties and reduce the number of rejected parts.
- Efficiency: Automated systems increase throughput and reduce cycle times.
- Waste Reduction: Accurate dosing minimizes raw material loss and cleanup costs.
- Quality: Advanced mixing and temperature control lead to superior end-product performance.