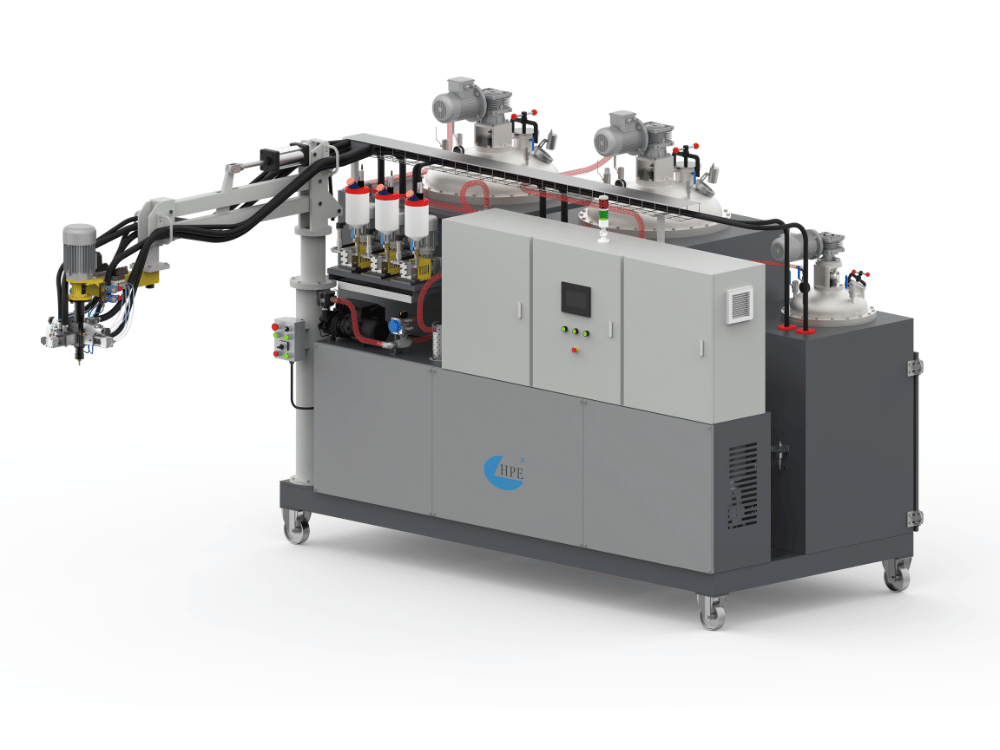
From industrial machinery components to consumer sporting goods, polyurethane elastomers are unsung heroes of modern manufacturing. The process of creating these durable and versatile parts is known as polyurethane elastomer casting, a method that transforms liquid chemicals into solid, high-performance products. The key to this transformation is the casting machine itself. This guide will provide an in-depth look at PU elastomer properties, the machinery used, and the incredible casting benefits that make this process so valuable.
Key benefits of polyurethane casting include:
- Durability and Abrasion Resistance: Creating parts that withstand wear and tear.
- Flexibility and Elasticity: Producing materials that can bend and stretch without breaking.
- Chemical and Oil Resistance: Ensuring longevity in harsh industrial environments.
What is Polyurethane?
Polyurethane (PU) is a highly versatile polymer created through the reaction of a polyol and an isocyanate. The unique properties of polyurethane allow it to take many forms, from rigid foams and flexible plastics to tough, rubber-like elastomers. This PU elastomer’s versatility makes it a preferred material for casting. By adjusting the chemical formulation, manufacturers can produce parts with a wide range of hardness, density, and elasticity, tailored to specific performance requirements.
Characteristics of Elastomers
Elastomers are polymers with viscoelasticity, meaning they possess both viscosity and elasticity. This gives them a “memory” that allows them to return to their original shape after being stretched or compressed. Key elastomer properties make them ideal for dynamic applications where resilience and durability are crucial. The main PU elastomer advantages include:
- High Elasticity: The ability to deform under stress and return to its original form.
- Excellent Abrasion Resistance: Superior toughness against scraping, rubbing, and erosion.
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Capable of supporting heavy loads without permanent damage.
- Impact Resistance: Absorbs energy from sudden shocks effectively.
Benefits of Casting with Polyurethane
Casting with polyurethane offers significant advantages over traditional materials such as rubber, metal, and plastic. One of the primary benefits of polyurethane casting is design flexibility; PU can be cast into complex shapes and sizes with relative ease and at lower tooling costs than injection molding. This makes it a cost-effective solution for both low-volume prototyping and high-volume production. Furthermore, the superior performance characteristics of PU provide longer service life for parts, making PU elastomer casting a clear choice for demanding applications.
The Polyurethane Elastomer Casting Machine
To fully grasp the capabilities and functionality of polyurethane elastomer casting machines, it’s essential to understand their individual components and how they work together. Each part, from the tanks to the mix head, plays a vital role in ensuring precise chemical processing and high-quality elastomer production. Let’s start by breaking down the key components of a casting machine and their importance in the overall process.
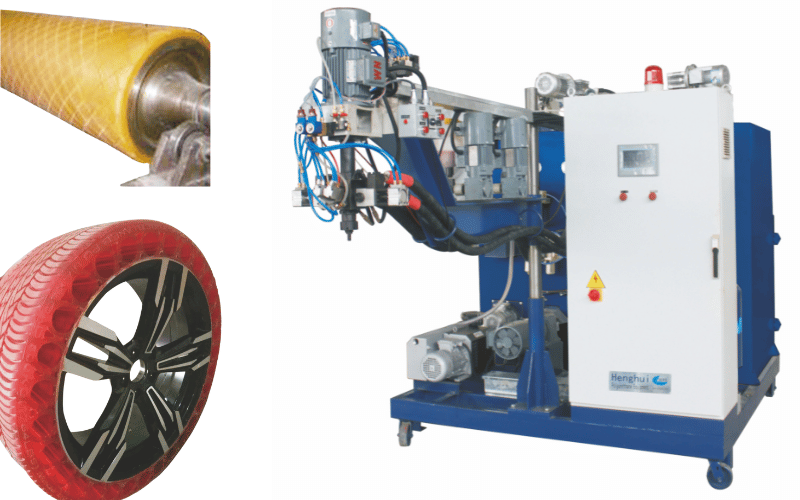
Components of the Casting Machine
A casting machine is a system of precisely engineered parts working together to process liquid polyurethane. Understanding these PU casting machine components is key to understanding the entire process. Each part plays a critical role in producing high-quality elastomer parts.
|
Component |
Function |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Tanks |
Store the polyol and isocyanate chemicals. |
Often heated and agitated to maintain proper temperature and consistency. |
|
Pumps |
Meter and deliver precise chemical ratios. |
Critical for ensuring the correct chemical reaction and final part properties. |
|
Mix Head |
Blends the two chemical streams. |
Ensures a homogenous mixture for uniform curing and performance. |
|
Control Panel |
Allows operators to set and monitor parameters. |
Provides control over temperature, pressure, and flow rates for process accuracy. |
Types of Polyurethane Casting Machines
There are several types of PU casting machines, each suited for different production needs. The main distinction lies in the operating pressure.
-
- High-Pressure Machines: Use impingement mixing at pressures over 1,500 PSI. They offer rapid, thorough mixing, making them ideal for high-volume production with fast cure times.
- Low-Pressure Machines: Operate at lower pressures and use a mechanical agitator in the mix head. They are better suited for smaller batches, slower pours, and applications that require more manual control.
- Manual Systems: For prototyping or tiny runs, chemicals can be mixed by hand and poured. This method offers the lowest cost but lacks the precision and consistency of high-pressure vs. low-pressure casting machines.
How the Machine Operates
The PU casting machine operation is a precise, multi-stage process. First, the two chemical components (polyol and isocyanate) are heated to their optimal processing temperatures in separate tanks. High-precision pumps then meter the chemicals at a specific ratio and deliver them to the mix head. Inside the mix head, the components are intensely blended. The liquid mixture is then dispensed into a pre-heated mold. Once in the mold, the chemical reaction continues, and the part cures, solidifying into its final shape. This entire elastomer casting process is carefully controlled to ensure consistent part quality.
Processing Techniques for Polyurethane Elastomers
The processing techniques used in polyurethane elastomer casting are critical to achieving the desired material properties and production efficiency. From high-pressure systems designed for speed and precision to low-pressure methods that offer greater control, each approach has its unique advantages. Let’s explore the key processing methods, including mixing, metering, and foaming techniques, that define the quality and versatility of PU elastomer casting.
High-Pressure vs. Low-Pressure Processing
The choice between high-pressure PU processing and low-pressure elastomer casting depends on the application, production volume, and material system. High-pressure processing is faster and more efficient for large runs, while low-pressure processing offers more control for complex or smaller parts.
|
Feature |
High-Pressure Processing |
Low-Pressure Processing |
|---|---|---|
|
Mixing Method |
High-speed impingement. |
Mechanical agitator. |
|
Cycle Time |
Very fast; suitable for automation. |
Slower; allows for more manual control. |
|
Waste |
Minimal; self-cleaning mix heads. |
It can have more waste and require solvent flushing. |
|
Ideal Use |
High-volume industrial parts. |
Prototyping, custom parts, and smaller batches. |
Mixing and Metering Systems
The quality of a cast elastomer part is directly tied to the accuracy of the chemical blend. Modern PU mixing systems and metering pumps are the core of this precision. High-precision gear pumps or piston pumps ensure that the polyol-to-isocyanate ratio is maintained within tight tolerances. Any deviation can lead to soft spots, brittleness, or incomplete curing. Achieving consistent metering accuracy in casting is therefore non-negotiable for producing reliable, high-performance parts.
Foaming Techniques in Elastomer Casting
While many elastomers are solid, some applications require a cellular or foamed structure to reduce weight or increase compressibility. These PU foaming techniques introduce a blowing agent into the chemical mix.
- Open-Cell Foaming: Creates an interconnected cell structure, resulting in a soft, breathable foam. This is used for cushioning and filtering applications.
- Closed-Cell Foaming: Creates sealed, individual cells, resulting in a rigid, water-resistant foam. This is common in elastomer foam casting for floatation devices or structural components.
Applications of Cast Polyurethane
Polyurethane elastomers are celebrated for their versatility, durability, and adaptability, making them indispensable across a wide range of industries. From industrial machinery to consumer products, cast polyurethane offers tailored solutions for both flexible and rigid applications. Let’s dive into the diverse uses of PU elastomers and explore the latest innovations driving advancements in casting technology.
Industrial Uses of PU Elastomers
The exceptional durability and resistance of polyurethane make it a go-to material for demanding industrial PU elastomer applications. It often replaces metal, plastic, and rubber in high-wear situations. Common PU elastomer uses in manufacturing include industrial rollers for conveyor systems, forklift wheels, seals, gaskets, and shock-absorbing pads for heavy machinery. These parts provide longer service life and reduce maintenance downtime.
Flexible and Rigid Polyurethane Applications
The versatility of polyurethane allows for both flexible and rigid parts, depending on the chemical formulation.
- Flexible PU Applications: These materials are soft and pliable, prized for their cushioning and elasticity. Examples include skateboard wheels, suspension bushings for vehicles, and comfortable armrests or handles.
- Rigid Polyurethane Uses: These are hard and structural, offering high impact strength and stiffness. Examples include protective housings for electronics, architectural moldings, and structural support components in various products.
Innovations in PU Casting Technology
The field of innovative PU casting is constantly evolving. Modern machines are incorporating IoT technology for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Automation through robotics is improving consistency and worker safety in advanced elastomer processing. There is also a growing focus on sustainability, with new bio-based polyols being developed from renewable resources to reduce the environmental footprint of polyurethane products.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Elastomer Casting Machines
Maintaining and troubleshooting polyurethane elastomer casting machines is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and high-quality output. Regular upkeep not only extends the lifespan of your equipment but also minimizes downtime and costly repairs. Let’s explore essential maintenance practices, common issues, and the benefits of upgrading to modern casting technology to keep your production running at peak performance.
Routine Maintenance Practices
Proper PU machine maintenance is essential for ensuring consistent operation and extending the life of your equipment. Key elastomer casting upkeep tasks include:
- Regularly cleaning the mix head to prevent chemical buildup and clogging.
- Checking and cleaning filters in the chemical lines.
- Inspecting pumps and seals for any signs of leaks or wear.
- Calibrating metering pumps to ensure ratio accuracy.
- Verifying that all heating elements and temperature sensors are functioning correctly.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even with proper maintenance, issues can arise. Knowing how to perform basic PU casting troubleshooting can save significant downtime.
|
Problem |
Possible Cause |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
Uneven Mixing |
Clogged mix head or incorrect pressure. |
Clean the mix head thoroughly and verify pump pressures. |
|
Off-Ratio Pour |
Pump malfunction or incorrect calibration. |
Recalibrate the pumps and inspect them for wear. |
|
Air Bubbles in Part |
Moisture contamination in chemicals or mold. |
Store chemicals in sealed containers and ensure molds are dry. |
|
Slow Curing |
Incorrect temperature of chemicals or mold. |
Verify that all heating systems are set to the correct temperature. |
Upgrading Your Casting Equipment
As technology advances, upgrading PU machines can offer substantial benefits. Modern equipment often provides better process control, higher efficiency, and improved safety features. Advanced elastomer casting equipment with automation capabilities can reduce labor costs and increase throughput. An upgrade can also enhance data logging and quality control, helping you produce better parts more consistently and stay competitive in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are polyurethane casting machines, and how do they fit into manufacturing processes?
Polyurethane casting machines are processing equipment designed to mix, heat, pump, and pour polyurethane resins or MDI-based systems into molds for producing elastomer products, foam parts, seals, and a wide range of cast PU items. In modern manufacturing, they automate injection or low-pressure pour methods, increasing productivity and consistency compared with manual casting. These machines for PU integrate components such as mixers, pumps, heating circuits, and PLCs or programmable controls to manage cycle times, temperature, and pressure, enabling repeatable, high-quality parts across manufacturing processes.
What types of molding methods do polyurethane casting machines support?
PU processing machines support several molding methods, including resin casting, injection molding, pour casting (low-pressure/hand pour), high-pressure injection, and PU foaming for pressure polyurethane foam parts and insulation. Many systems can switch between injection system and low-pressure pour modes or combine spray and pour techniques, offering flexibility to handle viscous elastomers, rubber-like urethanes, and open- or closed-cell foam chemistries.
How do machines ensure bubble-free, flawless castings and degas results?
To deliver bubble-free, flawless parts, polyurethane casting machines use high-precision mixing methods, inline degas stages, controlled heating, and accurate pump pressure control. High-quality mixers and metering pumps maintain the exact component ratio and shear to avoid air bubble entrapment; degassing chambers and vacuum-assisted mixing remove dissolved air before injection. Programmable cycles, pressure ramps, and material heating at controlled high temperatures help reduce viscosity and prevent bubbles, ensuring consistent hardness and surface finish.
What is the difference between high-pressure and low-pressure PU casting systems?
High-pressure systems use powerful pumps and high-pressure injection to quickly fill complex molds, often enabling shorter cycle times and finer detail reproduction, suitable for high-precision parts and tough elastomer products. Low-pressure machines pour or inject at reduced pressures, minimizing mold flash and tooling stress, preferred for large castings, pressure polyurethane foam, and softer urethane parts. The choice depends on part geometry, material properties, mold durabilit,y and required precision.
How do polyurethane machines improve efficiency and reduce manual labor?
Modern casting machines automate mixing ratios, heating, injection timing, and degassing via PLC controls and programmable interfaces, which reduces manual labor and operator variability. Integrated mixers, automatic pumps, and programmable cycles increase throughput, shorten cycle times, and raise productivity while maintaining high precision. Automation also enables repeatable control of material properties (hardness, density, viscosity) over decades of production, allowing manufacturers to scale without sacrificing quality.
What material considerations (raw material and resin) should be made when selecting machine technology?
Select machines based on the chemistry (MDI, TDI, polyol blends), viscosity, and required additives or solvents. Equipment must accommodate the raw material’s temperature sensitivity—requiring heating systems for viscous resins and high-temperature operation for some chemistries—and provide appropriate seals and materials in contact areas to resist solvents and reactive components. Machine manufacturers offer tailored pumps, metering heads, and mixers that preserve material properties and prevent contamination for high-quality castings.
Can polyurethane casting machines handle both foam and solid urethane parts?
Yes. Many processing machines are configurable for PU foaming (pressure polyurethane foam) and solid urethane casting or injection. By adjusting injection system parameters and mixing ratios, and by adding specialized foaming heads or spray attachments, a single machine can produce insulation foam panels, structural foam cores, rubber-like elastomer parts, and cast PU components. This flexibility makes the machinery compact and integral to diverse production lines.
How important is precision in pumps, mixers, and control systems for achieving consistent product quality?
High precision in pumps and mixers is critical: accurate metering maintains the correct stoichiometry of reactive components, mixing method and shear affect final hardness and mechanical properties, and PLC controls ensure consistent cycles and temperature profiles. Precise equipment reduces rejects, prevents bubbles, and provides material properties such as elongation, tear strength, and Shore hardness that remain within spec—key for applications where tolerances and functionality matter.
What maintenance and safety considerations should be expected from machine manufacturers?
Machine manufacturers typically recommend routine maintenance of pumps, seals, heating elements, and mixers, periodic calibration of metering systems, and inspection of electrical and mechanical components. Safety measures include solvent-handling protocols, ventilation for fumes, controls for high-pressure operations, emergency stops, and interlocks. Proper training on manual and automated procedures reduces the risk of defects such as bubbles or improper curing and ensures long-term efficiency and reliability of the processing equipment.